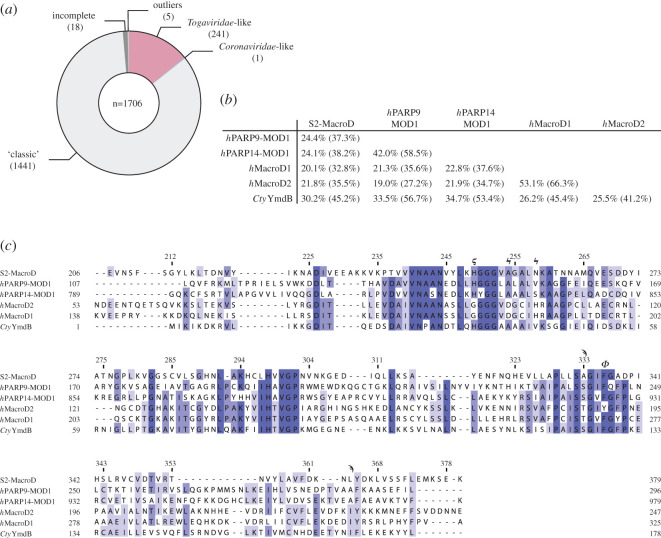
Figure 7.
Assessment of similarities between viral, human and human-associated microbiome macrodomains. (a) The members of the human microbiome encode only a limited number of viral-like macrodomains. Sequences extracted from the MGnify database were aligned and classified according to the three identified catalytic motifs (compare figure 5a). Sequences denoted as incomplete lack either the aspartate or histidine from the ‘classic' motif and outliers have none of the catalytic residues. (b) Pairwise sequence identity comparison of S2-MacroD with closest human relatives (MOD1 of hPARP9 and 14 as well as hMacroD1 and 2) as well as the only identified Coronaviridae-like macrodomain from the human microbiome (Clostridium tyrobutyricum YmdB, CtyYmdB). Sequence identity and similarity (in parentheses) are provided. (c) Multiple sequence alignment of sequences analysed in (b). Important residues are indicated underneath the alignment: ‘classic' (ϟ) and Coronaviridae catalytic residues (ϛ), active site arene (ϕ) and residues involved in proximal ribose coordination (ϡ).