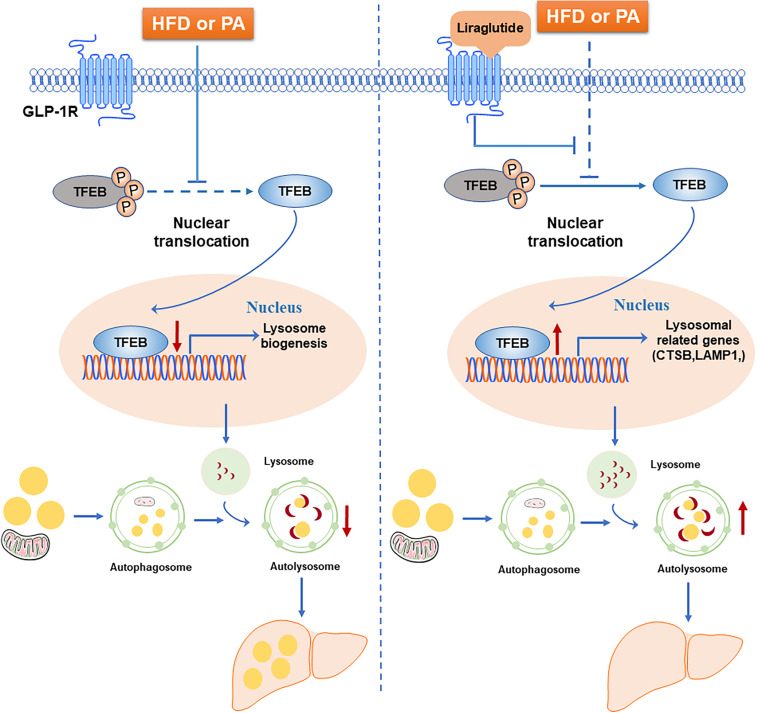
FIGURE 9.
Schematic diagram of the mechanism of liraglutide-mediated alleviation of hepatic steatosis. HFD or PA exposure inhibits TFEB dephosphorylation and nuclear translocation. TFEB regulates lysosomal biogenesis and function. The blocking of TFEB nuclear translocation leads to autophagic flux impairment and subsequently aggravates hepatic steatosis. Liraglutide, a GLP-1R agonist, alleviates hepatic steatosis through enhancing autophagic flux. Mechanistically, liraglutide activates TFEB and its downstream targets through activation of GLP-1R.