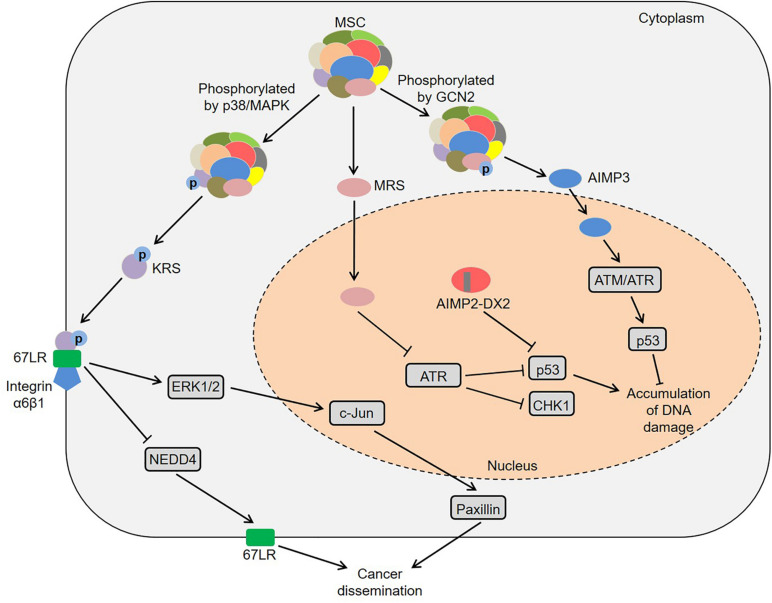
FIGURE 1.
Common pathways mediated by ARSs in cancer development. KRS is phosphorylated by p38/MAPK and then dissociates from the MSC. Subsequently, the KRS interacts with 67LR that is localized in the cell membrane, which prevents NEDD4 from ubiquitinating 67LR and enhances laminin-induced cell migration. Moreover, KRS forms a complex with 67LR and integrin α6β1 to mediate ERKs/c-Jun activation and paxillin expression. MRS increases the lysine homocysteinylation of ATR, thereby inhibiting ATR and its downstream CHK1 and p53. AIMP2-DX2 reduces the pro-apoptotic activity of AIMP2 by competitively binding to p53 with AIMP2. Furthermore, MRS is phosphorylated by GCN2, resulting in a conformational change of MRS and subsequent dissociation of AIMP3 from the MSC. The released AIMP3 interacts with ATM/ATR to up-regulate the expression of p53, thereby responding to DNA damage. ARSs, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases; AIMPs, ARS-interacting multifunctional proteins; KRS, lysyl-tRNA synthetase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MSC, multi-tRNA synthetase complex; 67LR, 67-kDa laminin receptor; NEDD4, neural precursor cell expressed developmentally downregulated 4; ERKs, extracellular signal-regulated kinases; MRS, methionyl-tRNA synthetase; ATR, ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related protein; CHK1, checkpoint kinase-1; AIMP2-DX2, AIMP2 lacking exon 2; GCN2, general control non-repressed-2; ATM, ataxia telangiectasia-mutated.