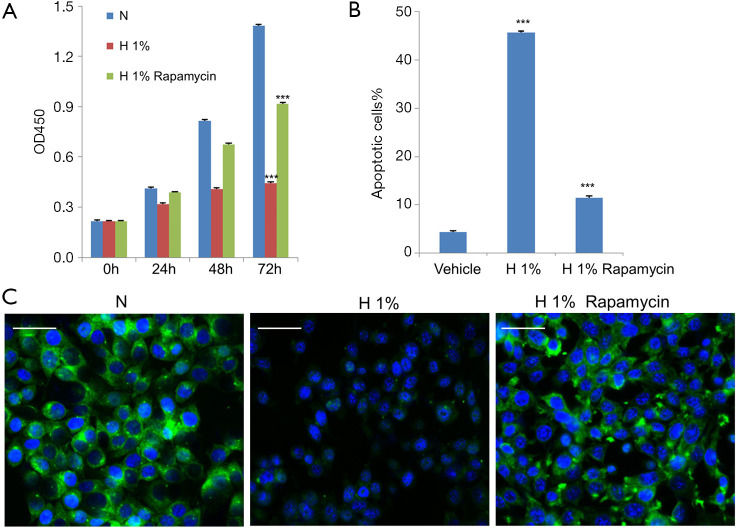
Figure 1.
Hypoxia induced apoptosis and inhibited autophagy in D407 cells. (A) Cell growth was inhibited by hypoxia (1% O2) over 72 h, and was partially recovered by the administration of rapamycin (100 nM). (B) Hypoxia increased apoptosis compared to normoxia, which was inhibited by the addition of 100 nM rapamycin. After having been subjected to hypoxia in the presence or absence of rapamycin for 48 h, human D407 RPE cells were collected and analyzed with fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). (C) The autophagy marker LC3 was measured with fluorescence microscopy after treatment with hypoxia for 48 h. Hypoxic treatment decreased the immunofluorescence of LC3 (green), which was reversed by rapamycin (100 nM). The nuclei were stained with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) in blue. Scale bar: 50 μm. Asterisks indicate significant difference (***, P<0.001).