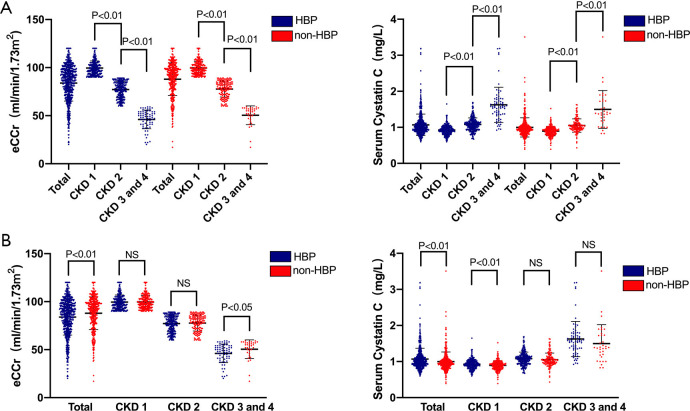
Figure 1.
eCCr and serum CysC of total study patients, including patients with different renal functions classified by CKD staging. (A) With decreased renal function, the serum CysC increased across CKD stages in both the HBP and non-HBP groups; (B) across the total cases, serum CysC was higher in patients with hypertension (1.07±0.30 vs. 1.00±0.27 mg/L, P<0.01) and eCCr was lower in patients with hypertension (83.89±18.69 vs. 87.95±17.04 mL/min/1.73 m2, P<0.01). In CKD stage 1 patients, serum CysC was higher (0.93±0.13 vs. 0.89±0.13 mg/L, P<0.01) in patients with hypertension, while no statistically significant difference in eCCr was found between groups. In CKD stage 2–4 patients, there was no statistically significant difference in serum CysC between the two groups. CKD, chronic kidney disease; eCCr, endogenous creatinine clearance rate; HBP, hypertension; CysC, cystatin C.