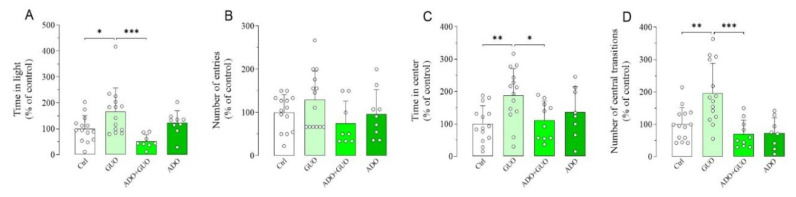
Figure 4.
Anxiolytic-like effect of GUO evaluated by light–dark box (LDB) and open field test (OFT) test during a 5 min session. (A,B) The LDB data analysis revealed that GUO treatment (30 mg/kg) significantly increased the time spent in light box, as compared to control (Ctrl) group, whereas the number of entries although increased did not become significant. This anxiolytic-like effect of GUO treatment was completely blocked by pretreatment with nonselective ARs agonist ADO. ADO treatment alone did not affect behavior as compared to control group. (C,D) The OFT data analysis revealed that GUO treatment (30 mg/kg) significantly increased both the number of central transitions and the amount of time spent in the center of the arena compared to control group. This anxiolytic-like effect of GUO was completely blocked by pretreatment with ADO, and ADO treatment alone did not affect behavior as compared to control group. LDB: time in light [F(3,41) = 6.146, p < 0.002], number of entries [F(3,41) = 1.843]. OFT: time in center [F(3,42) = 4.330, p < 0.01], number of central transitions [F(3,42) = 9.930, p < 0.0001]. Each bar represents the mean value ± SD. Tukey test: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.005, *** p < 0.0005. Ctrl raw mean values: (A) 26.69 s; (B) 2.29; (C) 24.29 s; (D) 8.86.