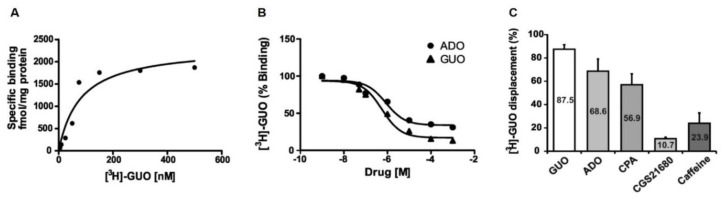
Figure 5.
[3H]GUO binding to hippocampal membranes. (A) The saturation isotherm studies showed that the binding became saturable at [3H]GUO concentrations ranging between 100 and 300 nM. The pooled data resolved for the presence of a single high affinity binding site with an apparent KD = 80 ± 34 nM; Bmax= 2339 ± 339 fmol/mg /protein. (B) Displacement of [3H]GUO binding by GUO and nonselective ARs agonist ADO in rat hippocampal membranes. Competition binding between GUO and ADO showed for ADO almost the same potency order of GUO to displace [3H]GUO (pIC50 6.069 ± 0.2074 and pIC50 −6.251 ± 0.1649, respectively), although ADO was able to displace only 70% of [3H]GUO binding. (C) [3H]GUO displacement (70 nM) by 500 µM of GUO, ADO, caffeine and selective agonists CPA or CGS21680 in rat hippocampal membranes.ADO was almost as effective as GUO in displacing [3H]GUO binding. Selective A1R agonist CPA or selective A2AR agonist CGS21680 displaced respectively 57% and 11% of [3H]GUO binding. Nonselective ARs antagonist caffeine displaced only 24% of [3H]GUO binding.