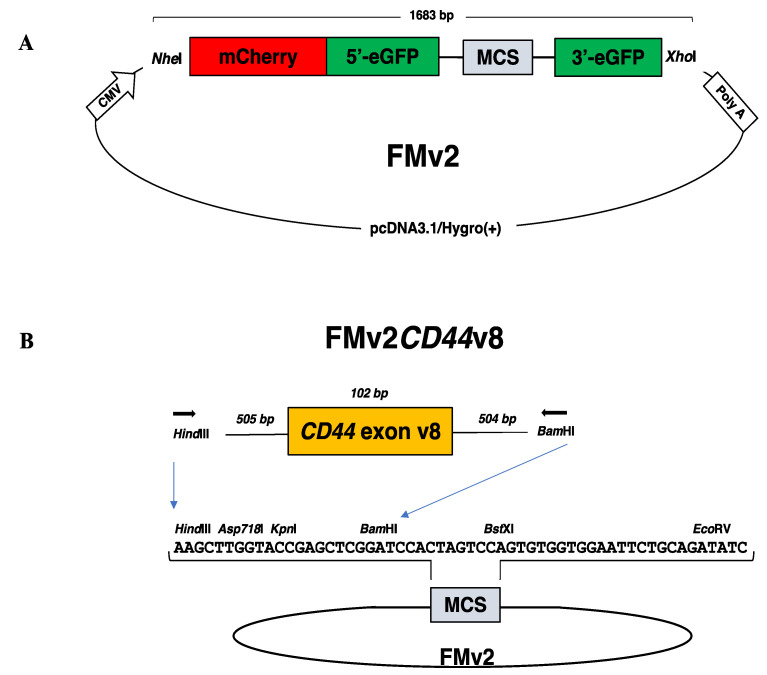
Figure 1.
Dual fluorescence-based splicing reporter minigenes. (A) The structure of a ready-made dual fluorescence-based splicing reporter minigene is schematically described. An expression vector pcDNA3.1/Hygro(+) encoding the CMV promoter (CMV) and the polyadenylation signal of bovine growth hormone gene (poly A) was inserted with the synthesized 1683 bp long fragment with the use of NheI and XhoI restriction enzymes. The synthesized DNA comprised of sequences of the NheI restriction enzyme recognition site, mCherry, the 5′ region of eGFP (5′-eGFP), the 5′-end of DMD intron 18, the multicloning site (MCS), the 3′-end of DMD intron 19, the 3′ region of eGFP (3′-eGFP), and the XhoI restriction enzyme recognition site. The MCS sequence is immediately flanked upstream and downstream by the first part of DMD intron18 and the last part of DMD intron19, respectively. The original construct named as FM was modified to create FMv2 by replacing 15 nucleotides. (B) The ready-made minigene (FMv2) was modified to produce FMv2CD44v8 as follows. PCR amplified genomic region of exon v8 of the CD44 gene was inserted into the MCS of FMv2 using HindIII and BamHI restriction enzymes. The sequence of the MCS is described in the middle together with restriction enzyme recognition sites. Exon v8 of the CD44 gene (102 bp) and its flanking introns (505 and 504 bps, respectively) were amplified using primers (horizontal arrowhead) with HindIII and BamHI sequences added at the 5′end.