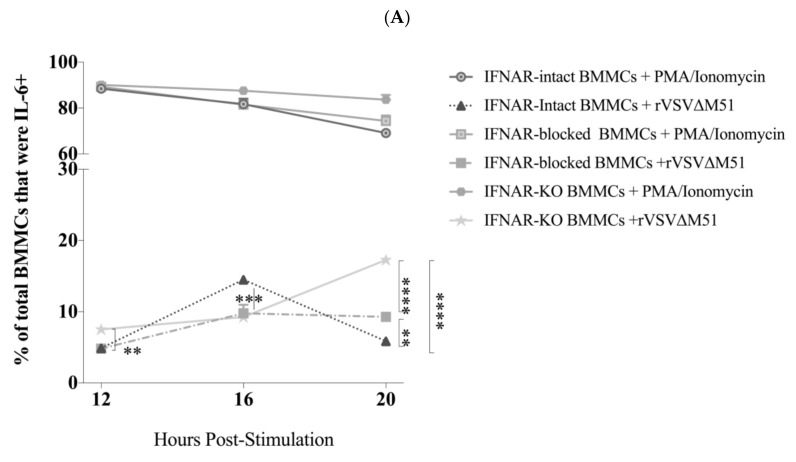
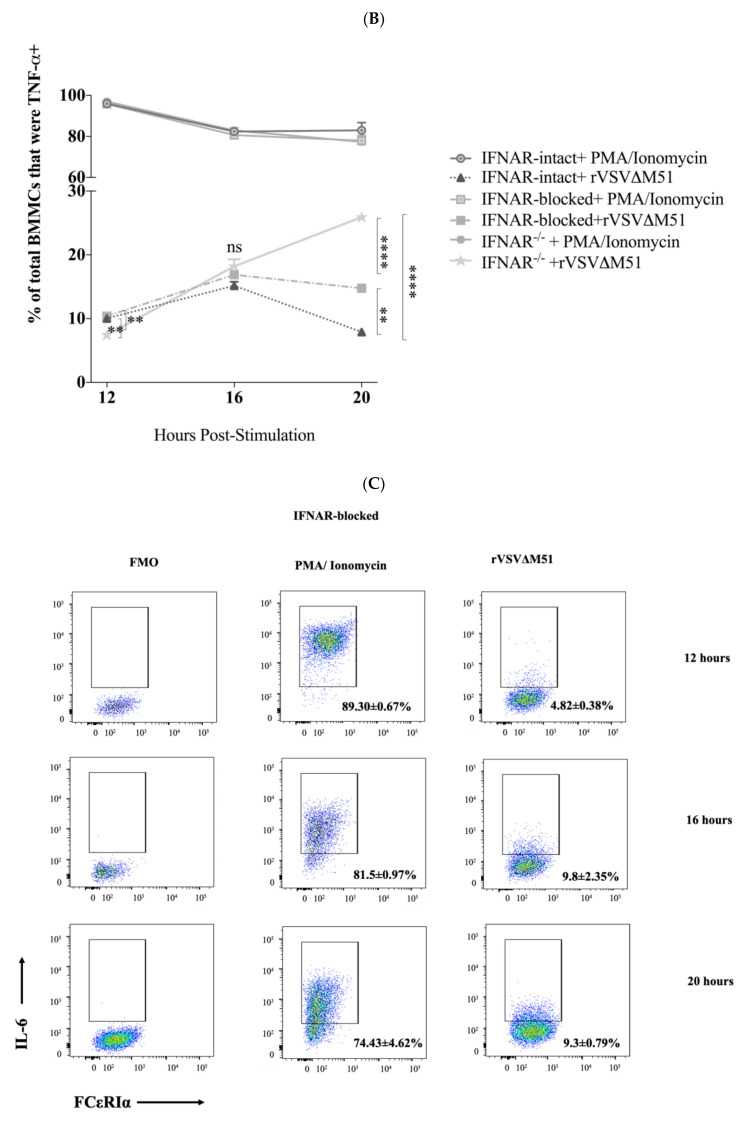
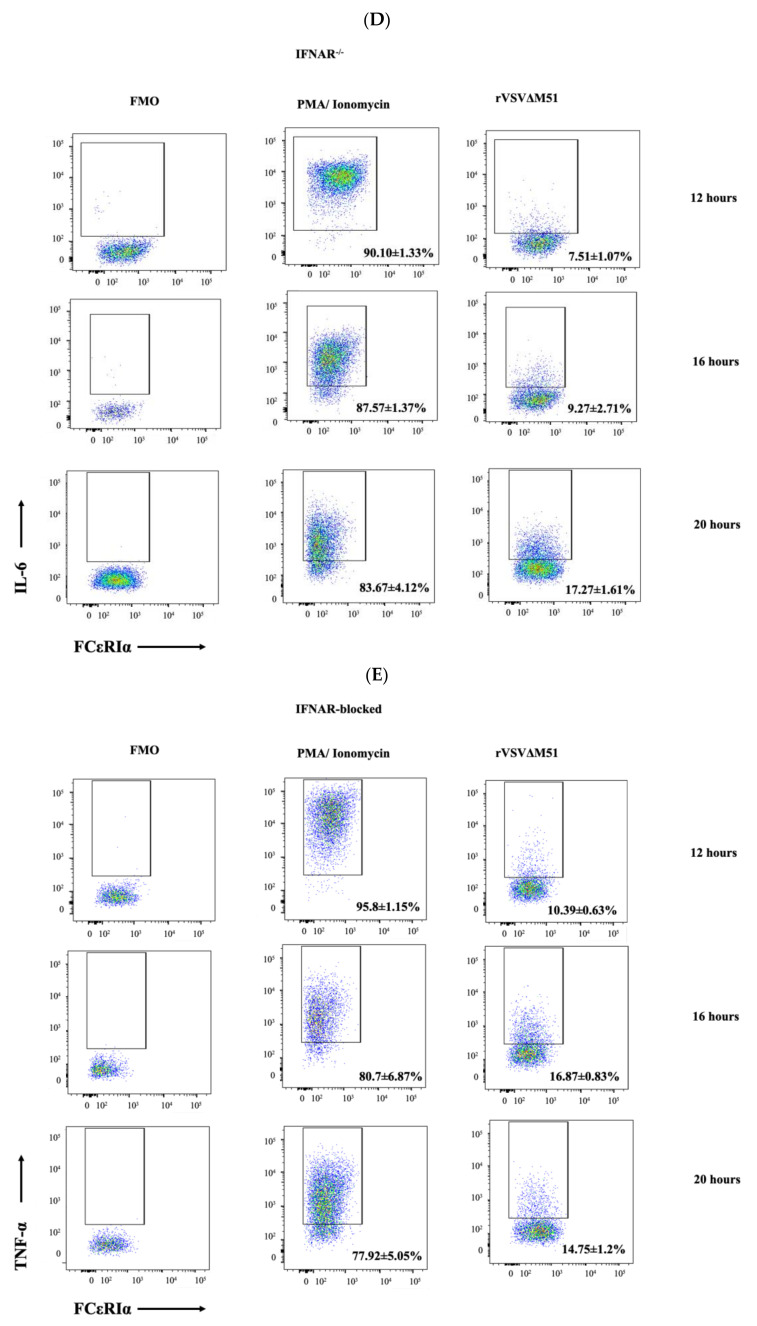
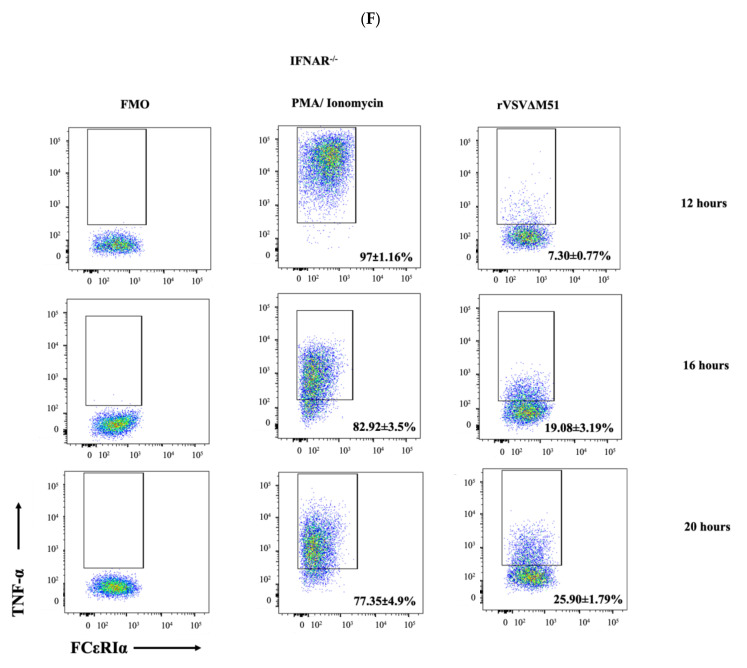
Figure 5.
Recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus (rVSVΔm51)-induced cytokine production by murine bone-marrow-derived mast cells (BMMCs) was regulated by type I interferon receptor (IFNAR) signaling. BMMCs that were left untreated (intact BMMCs) or incubated with an antibody that blocked IFNARs (IFNAR-blocked BMMCs) or derived from IFNAR-knockout mice (IFNAR−/− BMMCs) were infected with rVSVΔm51 at a multiplicity of infection of 10. After 12, 16, and 20 h, the cells were stained for the surface markers FcεRIα and c-kit, as well as intracellular cytokines interleukin (IL)-6 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α. The cells were then analyzed by flow cytometry, and fluorescence minus one (FMO) controls were used to set gates to identify IL-6+ and TNF-α+ BMMCs. Expression of (A) IL-6 and (B) TNF-α expression in FcεRIα+c-Kit+ mast cells is shown after infection with rVSVΔm51 or treatment with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and ionomycin as a positive control stimulus. Graphs show means and standard deviations pooled from four (IFNAR-intact and -blocked BMMCs) or six (IFNAR−/− BMMCs) experimental replicates. Two-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s multiple comparison test was used to define statistical significance as ** p < 0.001; *** p < 0.0005; **** p < 0.0001. Representative dot plots of (C) IL-6 expression in IFNAR-blocked and (D) IFNAR−/− BMMCs as well as TNF-α expression in (E) IFNAR-blocked and (F) IFNAR−/− BMMCs are shown.