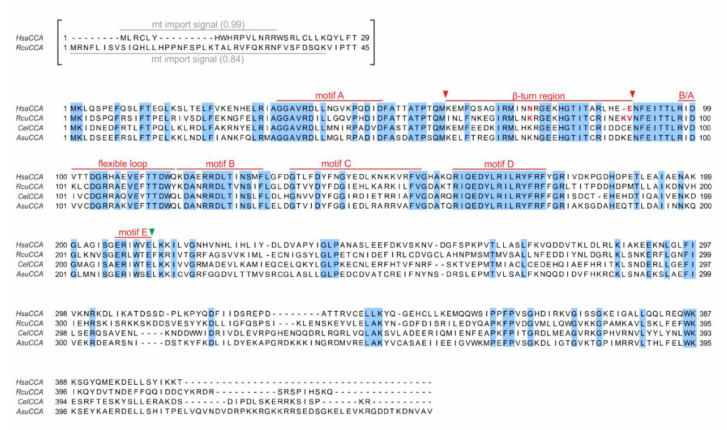
Figure 1.
Sequence alignment of CCA-adding enzymes from Homo sapiens, Romanomermis culicivorax, Caenorhabditis elegans, and Ascaris suum. Light blue positions indicate identical residues. The predicted mitochondrial import signals for H. sapiens CCA (HsaCCA) and the R. culicivorax CCA-adding enzyme (RcuCCA) (grey bars, import probability is given in brackets) are shown in brackets and were excluded from the cloned open reading frames. Catalytically important elements are labeled in red. Fusion position of reciprocal chimeras A and B are indicated by a green arrowhead. Fusion positions of chimera E (β-turn element) are indicated by red arrowheads (K/I61–E/V90). Mutations K74N and K89Δ/V90E introduced in RcuCCA and N74K and K89ins/E90V in HsaCCA are indicated in red.