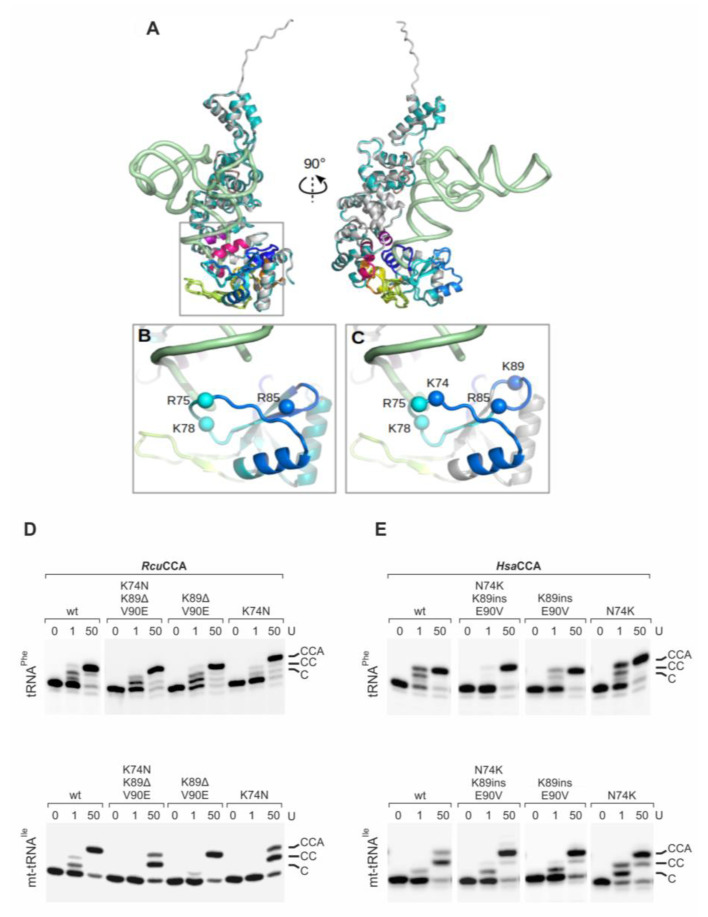
Figure 5.
The β-turn in HsaCCA and RcuCCA enzymes. (A) Superimposed full-length models of HsaCCA (cyan) and RcuCCA (light gray) with the backbone of a bound tRNA (green) in two perpendicular views. The tRNA position was obtained by superimposing the A-adding enzyme:tRNA-CC complex from Aquifex aeolicus onto the human enzyme [34,35,70]. Motif A (dark blue), β-turn region (medium blue), β-turn (light blue), B/A motif and flexible loop (green), motif B (yellow), motif C (orange), motif D (red) and motif E (violet) are indicated. (B,C). Zoom into the β-turn region and the tRNA 3′-end (corresponding to the squared region in (A) of HsaCCA (B) and RcuCCA (C). Spheres represent the Cα positions of positively charged residues (K and R). RcuCCA carries two additional lysines at positions 74 and 89 that might contribute to tRNA binding and primer positioning. Model is based on the crystal structure of the A-adding enzyme from Aquifex aeolicus [34]. (D) Enzymatic activity of RcuCCA carrying mutations K74N, K89Δ/V90E and K74N/K89Δ/V90E. 0, 1, and 50 arbitrary units of enzyme variants were incubated with yeast tRNAPhe and the armless mt-tRNAIle. RcuCCA wt accepts both tRNAs for CCA-addition, while RcuCCA K74N is less active on mt-tRNAIle, resulting in a considerably reduced A-addition. In contrast, RcuCCA K89Δ/V90E catalyzes full CCA-addition on the conventional (comparable to wt activity) as well as on the armless tRNA. The triple variant RcuCCA K74N/K89Δ/V90E shows the same activity as RcuCCA K74N. (E) The introduction of the corresponding amino acids of RcuCCA into HsaCCA enables this enzyme to add a complete CCA-end on mt-tRNAIle, in contrast to the wildtype situation. These results indicate that especially position K74 of the β-turn, but to a certain extent also K89/V90, contribute to the substrate adaptation of RcuCCA.