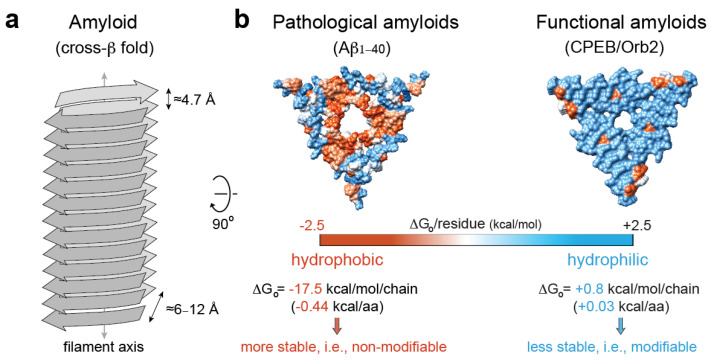
Figure 3.
Pathological vs. functional amyloids. (a) Structural traits of the cross-β amyloid fold [123]. (b) Hydrophobicity map on the molecular surface of a representative pathological amyloid, namely, β-amyloid1–40 in Alzheimer’s disease brain tissue (PDB code 2m4j [152]), vs. a functional, neuronal amyloid implicated in memory persistence (PDB code 6vps [9]), showing the different stabilization energy. The hydrophobic residues are colored red, and the hydrophilic ones are colored blue. The solvation energy calculations were obtained from ref. [153].