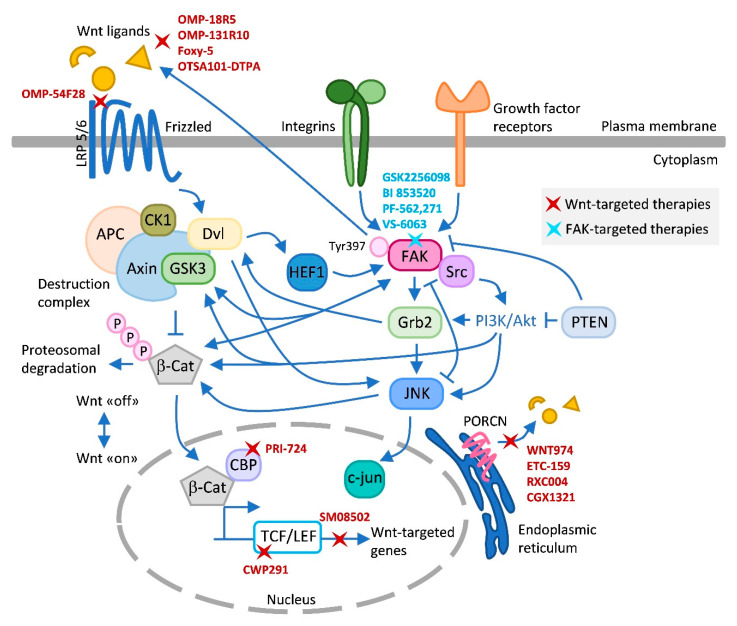
Figure 1.
Wnt–FAK signaling crosstalks and inhibitors. This figure summarizes the main known crosstalks existing between Wnt and FAK that have been described in the text and in the literature, and the different Wnt and FAK inhibitors tested in clinical trials. Upon FAK activation, the FAK/Src complex phosphorylates and recruits several downstream signaling targets, including PI3K/AKT. GSK3 generally acts as a downstream signaling protein molecule of AKT [152]. Grb2 coordinates signaling downstream of integrin/FAK to activate JNK. Grb2 also interacts directly with Dvl [153]. Dvl can stimulate c-Jun-dependent transcription activity and the kinase activity of JNK [154]. Loss of PTEN function causes the activation of PI3K/AKT and JNK pathways [155]. PTEN also controls FAK [148]. FAK and PYK2 promote Wnt/β-catenin pathway activation by phosphorylating GSK3β [74]. This phosphorylation inhibits the activity of GSK3β which otherwise would drive rapid degradation of β-catenin. FAK increases expression of Wnt ligands activating Wnt signaling and CSC self-renewal indirectly or directly by activating β-catenin [102]. In addition, FAK was shown to trigger the β-catenin signaling pathway through nuclear translocation of β-catenin and transcriptional activation of β-catenin target genes [74]. FAK and Wnt have been described to modulate each other antagonistically [84]. HEF1 localizes to focal adhesions to coordinate FAK/Src signaling and is also modulated by Wnt [80]. Wnt-targeted agents include OMP18R5, OMP131R10, Foxy-5, OTSA101-DPTA, and OMP-54F28, which target Wnt signaling at the ligand/receptor level; PRI-724, CWP291, and SM08502 at the transcriptional level; and the Porcupine inhibitors WNT974, ETC-159, RXC004, and CGK1321, which block Wnt ligand secretion. FAK inhibitors include GSK2256098, PF-562,271, and VS-6063, which competitively target the ATP-binding site K454, located in the kinase domain of FAK; and the competitive scaffold inhibitor BI 853520, which binds to the hinge region of the kinase domain of FAK blocking the access of ATP to the ATP binding site [143]. Arrows (↑) indicate activation/induction, and blunt-ended lines (T) indicate inhibition/blockade. LRP, low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein; Dvl, dishevelled; CK1, casein kinase 1; APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; GSK3, glycogen synthase kinase-3; β-Cat, β-catenin; CBP, CREB binding protein; TCF/LEF, T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor; Grb-2, growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; PORCN, Porcupine.