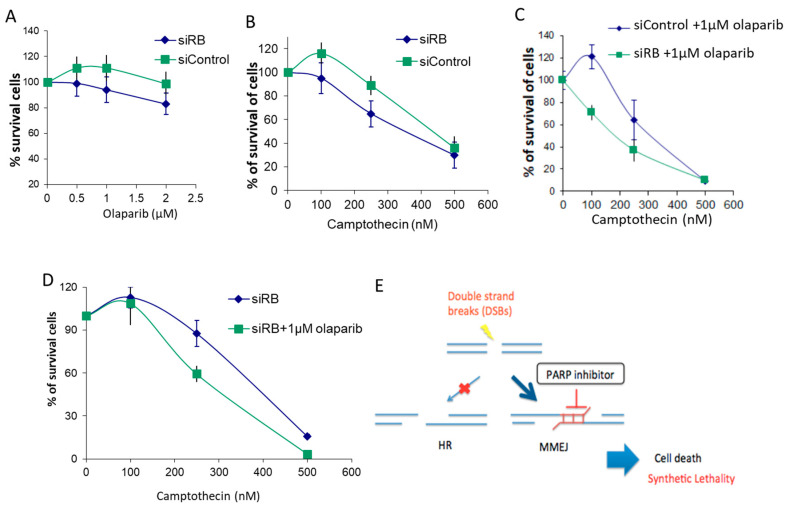
Figure 4.
RB knocked-down cells were hypersensitive to the combined treatment of poly-ADP ribose polymerase 1 (PARP1) inhibitor and camptothecin. (A): Cell survival was quantified by MTT assay in RB knocked-down cells with different dosages of olaparib for 3 days. (B): Cell survival was quantified by MTT assay in RB knocked-down and control cells treated with different dosages of CPT for 3 days. (C): Cell survival was quantified by MTT assay in RB knocked-down and control cells treated with different dosages of CPT with 1 μM olaparib for 3 days. (D): Cell survival was quantified by MTT assay in RB knocked-down cells with different dosages of CPT, with or without 1 μM olaparib, for 3 days. Mean values from three experiments are shown. Error bars show the standard error of the mean. Experiments were repeated three times. (E): RB-deficient cells are HR deficient and depend on MMEJ to repair DSB-repair. After DSB induction by CPT, PARP1 inhibitor could effectively block MMEJ, and led to enhanced cell death. The light red arrow indicates the HR pathway is inhibited in RB-deficient cells. The dark blue arrow indicates the MMEJ pathway is preferred in RB-deficient cells. The light blue arrow shows the synthetic lethality in RB-deficient cells treated with PARP inhibitor.