Figure 4.
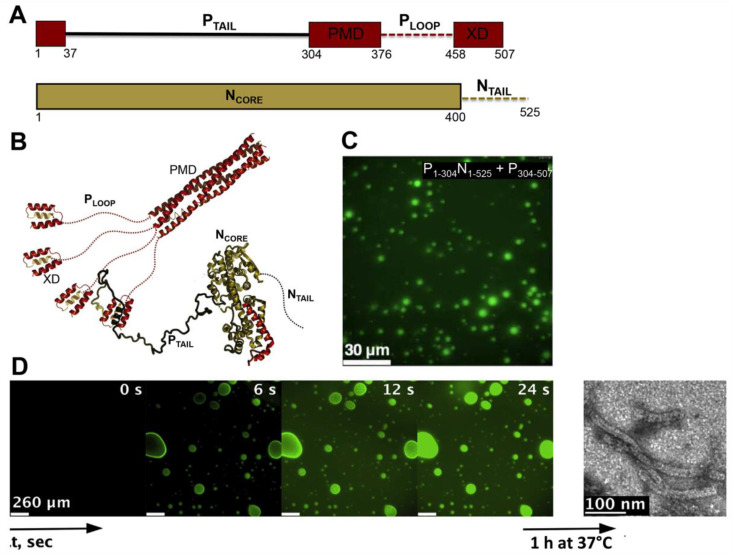
MeV N and P proteins form membrane-less organelles (MLOs) that colocalize with RNA and promote assembly of nucleocapsid-like particles. (A) Modular organization of the P and N proteins, where structured regions are shown as rectangles and disordered regions as dashed lines. The N-terminal module encompassing residues 1 to 37 corresponds to the Molecular Recognition element (MoRE) that binds to the monomeric form of the N protein while adopting a kinked α-helical conformation. PMD: P multimerization domain responsible for P tetramerization; XD, X domain. (B) Cartoon representation of the P region encompassing residues 304–507. Disordered regions are shown as dotted lines (modified from [183]). (C) Fluorescence microscopy image of a mixture containing fluorescein-labeled P1-304N1-525 and P304–507 where liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) occurs. (D) Fluorescence microscopy image showing fluorescently labeled RNA diffusing into droplets preformed by mixing P1−50N1−525 and P304−507. RNA colocalizes to N:P droplets and forms nucleocapsid-like particles, as observed by negative-staining electron microscopy after 1 h of incubation at 37 °C. Panels C and D reproduced with permission from [186].