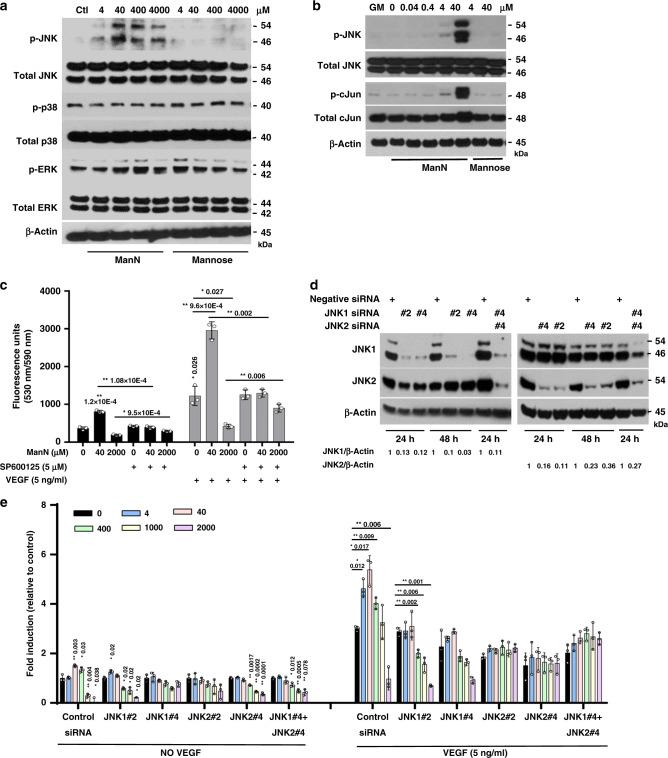
Fig. 3. ManN specifically activates the JNK pathway in BCECs.
a BCECs grown in growth media (GM: low-glucose DMEM containing 10% bovine calf serum (BCS), 10 ng/ml VEGF and 5 ng/ml bFGF) were switched to growth factor-free media, followed by treatment with ManN or Mannose at 4 μM–4 mM. Four hours later, cell lysates were collected and subjected to western blot analysis for phosphorylated JNK (Thr 183/Tyr 185), p38 (Thr 180/Tyr 182), and ERK (Thr 202/Tyr 204), as well as total JNK, p38, and ERK. b ManN, but not mannose, could activate JNK and its downstream c-Jun. β-actin served as the loading control. For each study, a representative experiment is shown from two to three independent studies. c BCECs plated in 96-well plates were attached, pre-treated with the specific JNK inhibitor SP600125 (5 μM) for 2 h, followed by ManN at either 40 μM or 2 mM, with or without 5 ng/ml VEGF. Six days later, cell proliferation was quantified after addition of AlamarBlue®. n = 3 independent samples. d Screening of siRNAs against JNK1 and JNK2. Twenty-four hours after siRNA transfection, BCECs were lysed and proteins were subjected to western blot analysis. β-actin served as the loading control. Quantification of target knockdown is shown. e A representative experiment shows that ~80% knockdown of JNK1 and/or JNK2 by two independent siRNAs was associated with a significant reduction in the stimulatory effects of ManN on BCEC proliferation. n = 3 independent samples. Data are means +/− SD, Asterisks indicated a significant difference compared with the control. When statistical analysis was done using a different control, a line was used between specific groups. Statistical analysis was done by two-tailed, two-sample unequal variance t test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Data are provided as a Source data file.