Figure 4. Glucose consumption in sperm from CatSper1 KO and in sperm treated with A23187.
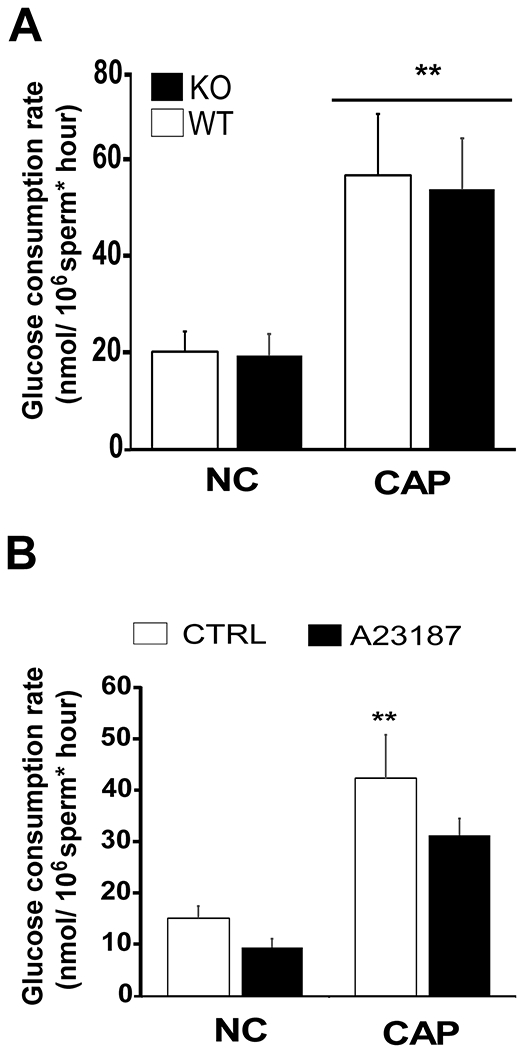
A) Cauda epididymal sperm from wild-type (WT, white column) or from CatSper1 KO mice (KO, black column) were separately obtained by swim-out and incubated in media that support (CAP) or not (NC) capacitation for 3 hours and glucose consumption ratio was determined as described in Methods. Data are shown as mean ± SEM of 7 independent experiments. Differences between treatments were analyzed by Bonferroni post-hoc test, **p < 0.01 indicates differences versus wild-type NC control. B) Spermatozoa obtained from CD-1 retired male breeders were allowed to swim-out in non-capacitating media, washed, suspended in the same media and treated with 20 μM 4Br-A23187 (black column) or with DMSO (white columns) for 10 min. At that point sperm become motionless in less than 1 minute. Ten minutes later, sperm were washed twice to remove the excess of 4Br-A23187 from the media and suspended in media supporting (CAP) (HCO3− 15 mM and 5 mg/mL BSA) or not (NC) capacitation. Sperm were then incubated for 3 hours and glucose consumption rates determined as described in Methods (n = 4). Differences between treatments were analyzed by Bonferroni post-hoc test, *p < 0.05 indicates differences versus NC control.
