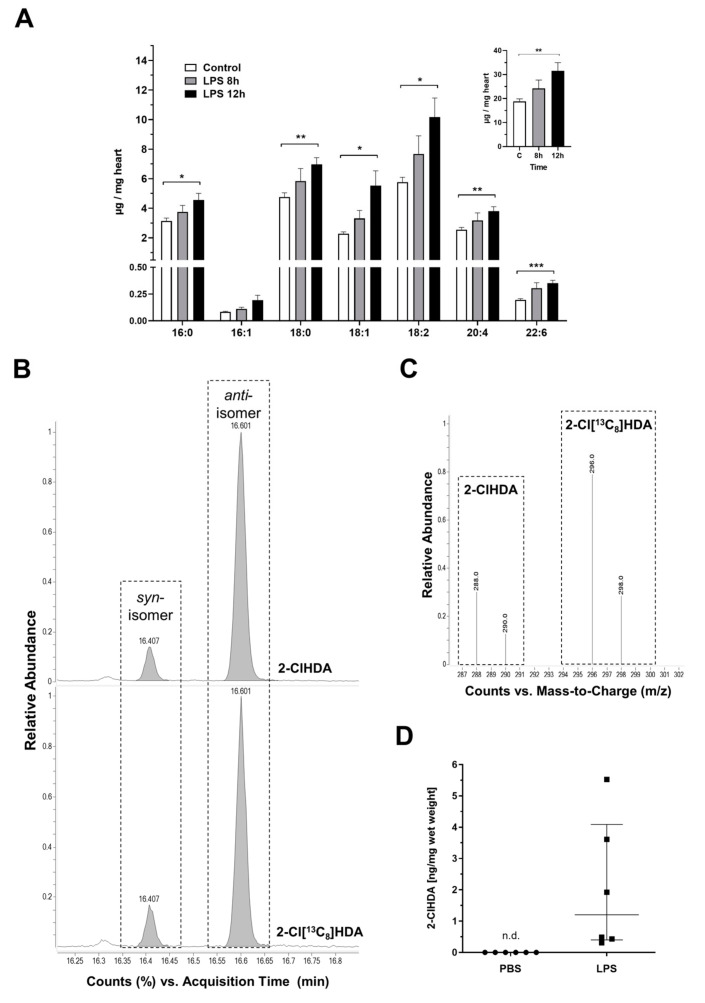
Figure 2.
Accumulation of various fatty acid (FA) species and 2-ClHDA in LPS-treated hearts. C57BL/6 mice received a single i.p. injection of PBS (200 µ) or LPS in PBS (from Escherichia coli, 0111:B4 in PBS, 8 µg/g body weight) and were sacrificed 8 or 12 h after the injection. (A) Cardiac FA composition of PBS- and LPS-injected mice was analyzed by gas chromatography. Inset shows total FA concentrations. Data represent mean + SEM; * p ≤ 0.05; ** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.001; unpaired student’s t-test (n = 5–6). (B–D) Cardiac 2-ClHDA concentrations were quantified by selected ion monitoring (SIM) NICI–GC–MS analysis using 2-Cl[13C8]HDA as internal standard. (B) SIM chromatograms of a representative cardiac lipid sample (top; 12 h post LPS treatment) and the synthetic standard (bottom). Boxed areas indicate the elution profiles of the syn- and anti-PFB-oxime derivatives of 2-ClHDA and 2-Cl[13C8]HDA. (C) Fragment ion intensity ratios of 2-ClHDA (m/z = 288, 290) and the internal standard (m/z = 296, 298) of the peaks highlighted in (B). (D) Formation of 2-ClHDA in the hearts of LPS-treated animals (n = 6) measured 12 h after a single systemic LPS injection. Lines represent median with interquartile range, unpaired student‘s t-test, non-detectable (n.d.).