FIGURE 1.
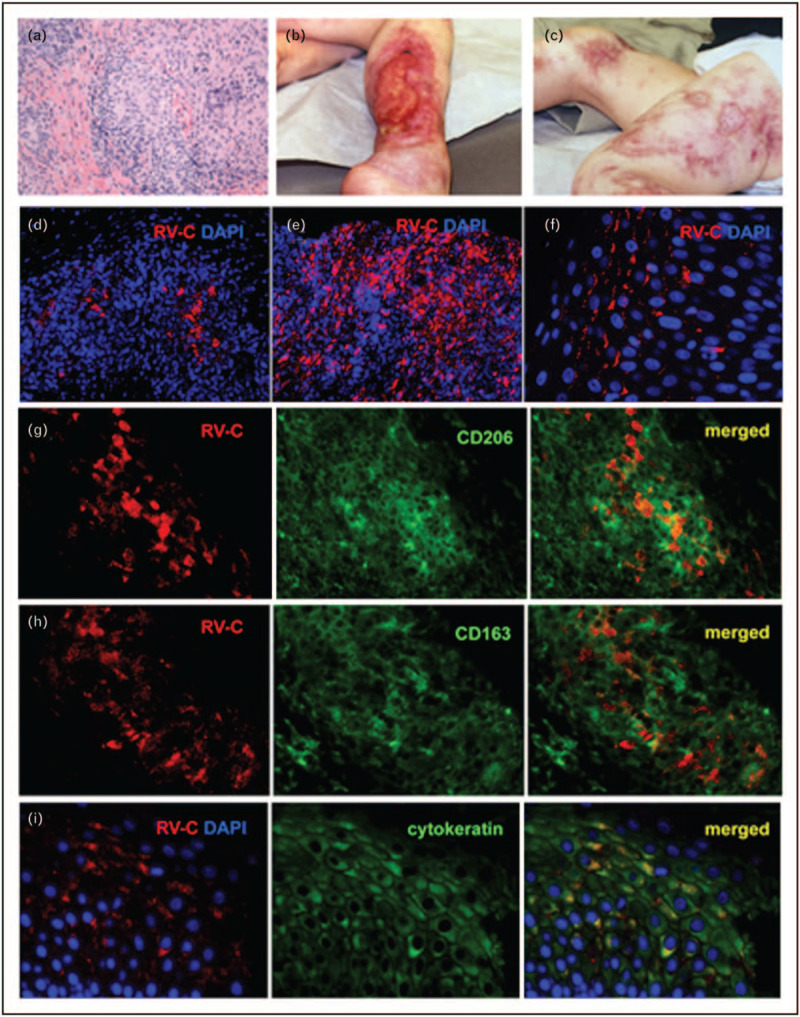
Cutaneous granulomas in PID patients. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of a cutaneous granuloma from case 1. A well-formed granuloma is centrally located. (b, c) Cutaneous skin lesions from case 3. Acute and chronic ulcers are observed. (d–f) Distribution of infected cells in skin samples of PID patients. Histological immunofluorescent staining showing focal (d, case 1) or widespread (e, case 2) distribution of RuV capsid in granulomas and focal capsid localization in the epidermis (f, case 5). Activation status of macrophages in granulomas (g–i, case 6). Double immunofluorescent staining of granulomas with RuV capsid antibody (red) and M2 macrophage specific antibodies, CD206 (g, green) or CD163 (h, green). (i) RuV antigen expression in the suprabasal cell layer of skin epidermis (case 1). Double immunofluorescent staining with RuV capsid antibody (red) and keratinocyte specific antibody (cytokeratin, green). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. Previously published in Ref. [8].
