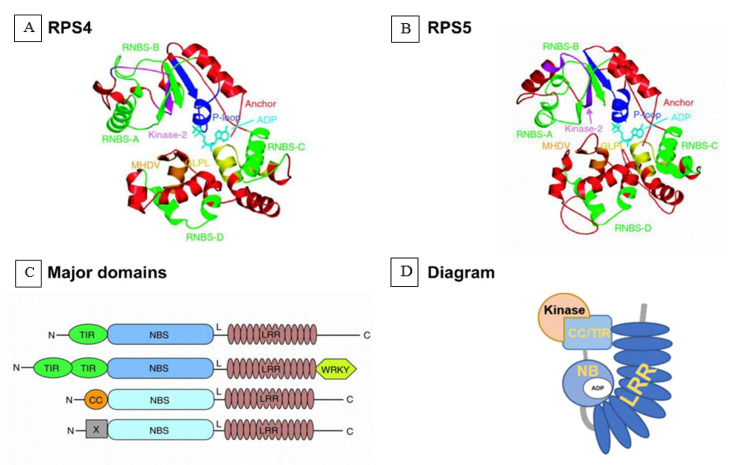
Figure 5.
Predicted structures and models of nucleotide-binding site domain and a leucine-rich repeat domain (NB-LLR). (A) The structures of the NBS domains (nucleotide-binding site domain and a leucine-rich repeat domain) of TNL and RPS4. The protein structures are shown as ribbon diagrams and ADP (adenosine diphosphate) is shown as a stick model. TIR-type and CC-type NBS domains are made up of motifs: P-loop (or Walker A site, blue), RNBS-A (green), kinase-2 (or Walker B site, magenta), RNBS-B (green), RNBS-C (green), GLPL (yellow), RNBS-D (green), and MHDV (orange) [131]. Structural models for the NBS domain of TNL RPS4 and CNL RPS5 of Arabidopsis were created by self-consistent mean-field homology modeling technique [132]. (B) The structures of the NBS domains of CNL RPS5; (C) major domains of NBL proteins. N, amino terminus; TIR, Toll/interleukin-1 receptor-like domain; CC, coiled-coil domain; X, domain without obvious CC motif; NBS, nucleotide binding site; L, linker; LRR, leucine-rich repeat domain; WRKY, zinc-finger transcription factor-related domain containing the WRKY sequence; C, carboxyl terminus; (D) Diagram of NLR.