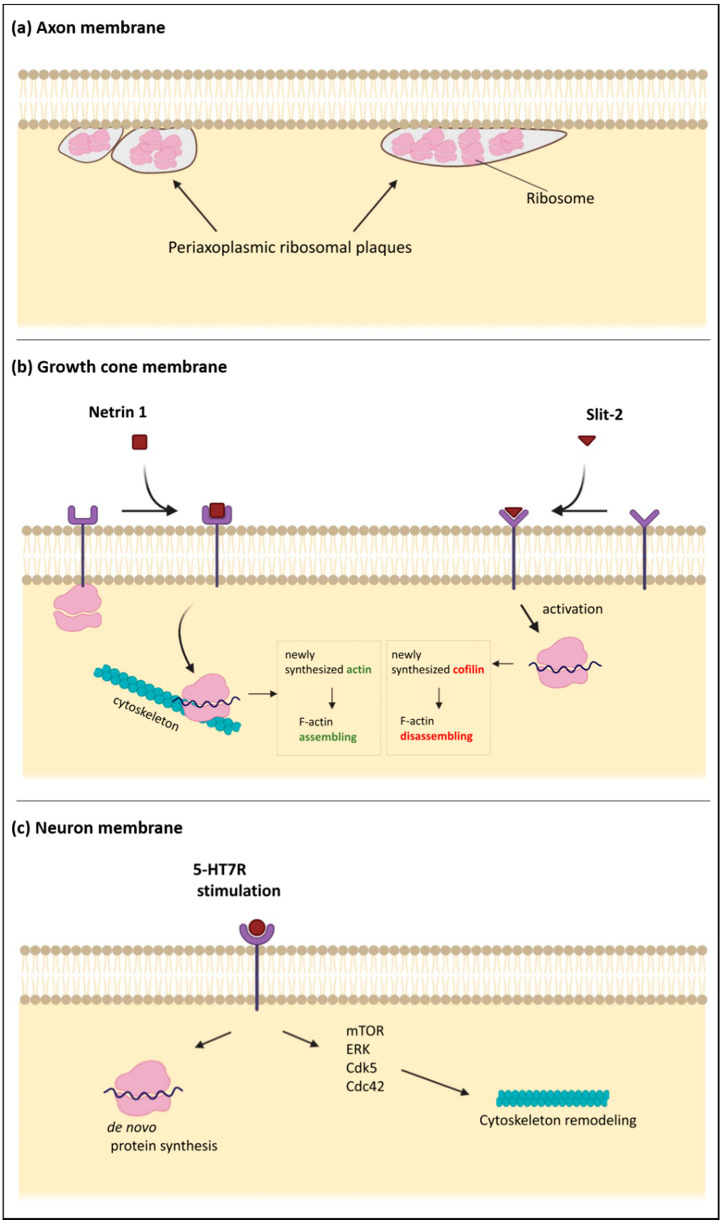
Figure 2.
Schematic diagrams of the subplasmalemmal regions in specialized neuronal compartments. (a) the axonal plasma membrane is associated with “periaxoplasmic plaques”, which contain ribosomes and therefore serve as a center for intra-axonal protein synthesis. (b) The plasma membrane of the growth cones contains receptors for various guiding cues. When netrin-1 receptor DCC (Deleted in Colorectal Carcinoma) is bound by netrin, the sequestered ribosomes are released from the membrane and move to the unspecified cytoskeleton, which may serve as a scaffold for protein synthesis. Translation of β-actin mRNA increases local concentration of β-actin, which leads to enhanced F-actin polymerization. Binding of a repulsive guidance cue slit-2 has the opposite effect because of the increased local translation of cofilin, an actin-binding protein. (c) Stimulation of the serotonin receptor 7 (5-HT7R), localized in the neuronal plasma membrane, promotes de novo protein synthesis and activation of several signaling pathways such as ERK, Cdk5, Cdc42, and mTOR. These intracellular pathways converge to promote reorganization of the neuronal cytoskeleton, including microtubules and actin filaments.