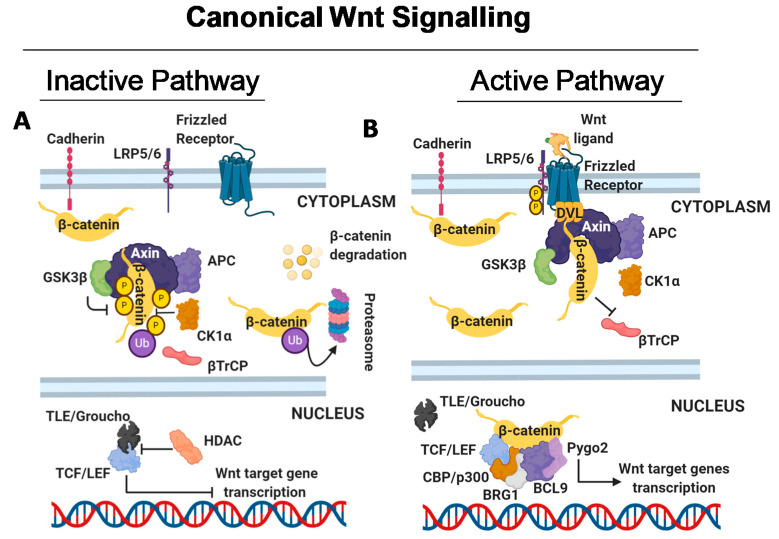
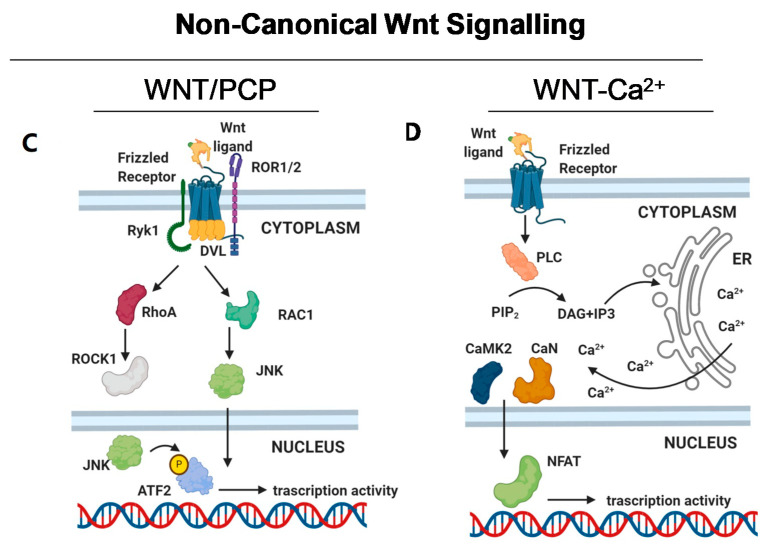
Figure 1.
Overview of canonical and non-canonical Wnt signalling. (A) In the canonical inactive wingless/integrated (Wnt) pathway, the absence of WNT ligands triggers the phosphorylation of β-catenin via the destruction complex consisting of Axin, adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), and the two kinases glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β) and casein kinase 1α (CK1α). In this biological scenario, β-catenin is phosphorylated by GSK3β and CK1α, ubiquitinated by β-transducin (β-TrCP), and targeted for proteasomal degradation, which impairs its nuclear translocation. In the absence of nuclear β-catenin, a repressive complex, consisting of T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor (TCF/LEF) and transducin-like enhancer of split (TLE)/Groucho, recruits histone deacetylase (HDAC) to halt Wnt target gene transcription. (B) The canonical active Wnt pathway is activated upon binding of WNT ligands to 15 Frizzled (FZD) receptors and LRP5/6 co-receptors. In this state, the destruction complex is recruited to the WNT/receptor complex and inactivated via the dissociation of all its components. This allows the stabilization and accumulation of cytoplasmic β-catenin, which then translocates into the nucleus where it forms an active complex with T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor (TCF/LEF) proteins by displacing TLE/Groucho complexes. Histone modifying co-activators, such as CREB-binding protein (CBP)/p300, Brahma Related Gene 1 (BRG1), B-cell CLL/lymphoma 9 (BCL9) and Pypgpus family PHD finger2 (Pygo2), are recruited, thus allowing the transcription of the Wnt target genes. (C) In non-canonical Wnt/planar cell polarity (PCP) signalling, WNT ligands bind to the Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Like Orphan Receptor (ROR)/FZD complex, thus recruiting and activating Dishevelled (DVL). This triggers activation of the small GTPases Ras homolog family member A (RhoA) and Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (RAC1), which in turn activate Rho Associated Coiled-Coil Containing Protein Kinase (ROCK) and c-Jun N-terminal Kinase (JNK), leading to rearrangements of the cytoskeleton and transcriptional program via activating transcription factor 2 (ATF2). (D) Wnt/Ca2+ signalling is initiated by G-protein triggered phospholipase C (PLC), which converts phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol trisphosphate (IP3). This leads to intracellular calcium fluxes and, in turn, activation of calmodulin kinase 2 (CaMK2) and calcineurin (CaN) proteins to induce downstream calcium-dependent cytoskeletal modifications and transcriptional activity via the activating factor nuclear factor of activated T-cell (NFAT).