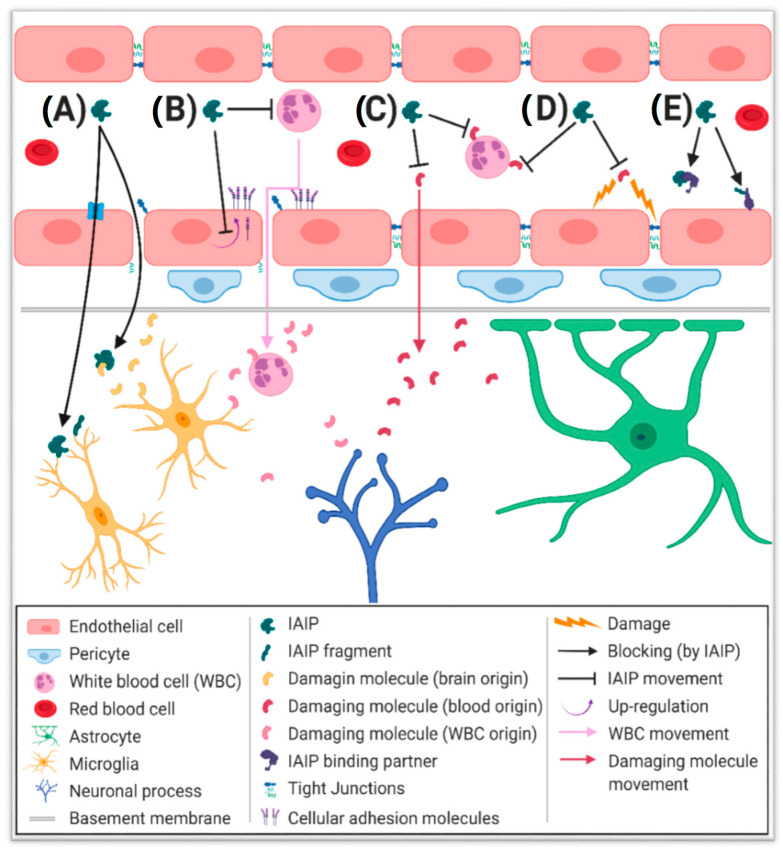
Figure 2.
Stylized schematic of potential mechanisms underlying the neuroprotective properties of inter-alpha inhibitor protein (IAIP) treatment after exposure to hypoxia-ischemia (HI) in neonatal subjects. Legends for the elements in the Figure are illustrated below the Figure. The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is shown with endothelial cells joined by tight junction proteins. Red blood cells and white blood cells are depicted in the bloodstream. Pericytes line the vascular endothelium below the basement membrane. Astrocytes have endfeet that line the neurovascular unit, microglia, and neuronal processes are also in close proximity to the vasculature. The potential actions of IAIPs are also shown: (A) IAIPs or smaller subunit components of IAIPs could cross the BBB through paracellular transfer that is increased after HI damage or through yet to be identified transcellular pathways. Once within the central nervous system (CNS), IAIPs or IAIP components could interact with molecules or cells within the brain directly; (B) IAIPs might attenuate the transfer of activated immune cells into the brain by limiting the up-regulation of adhesion molecules on endothelial cells, altering the ability of immune cells to cross the vasculature or transforming immune cells to a non-damaging phenotype; (C) IAIPs may limit the transfer of harmful molecules into brain tissue by either directly inactivating the molecule or by preventing its production, release, or BBB passage; (D) Through similar mechanisms in (C), IAIPs might decrease the amount of harmful molecules in the systemic circulation, thereby preventing those molecules from damaging the integrity of the BBB; (E) IAIPs or components of IAIPs may form molecular complexes that either cross the BBB, line the BBB vasculature, or have downstream effects independent of the original IAIP molecule administered. Although the potential mechanism(s) of action of IAIPs depicted in (A–E) have some support, as summarized above, many of the specific molecular mechanism(s) at the BBB endothelium require future investigation. Cellular and molecular size, distribution and neurovascular coverage are not necessarily accurately depicted to allow for illustration of the potential mechanism(s) of action of IAIPs. Illustration was created with BioRender.com.