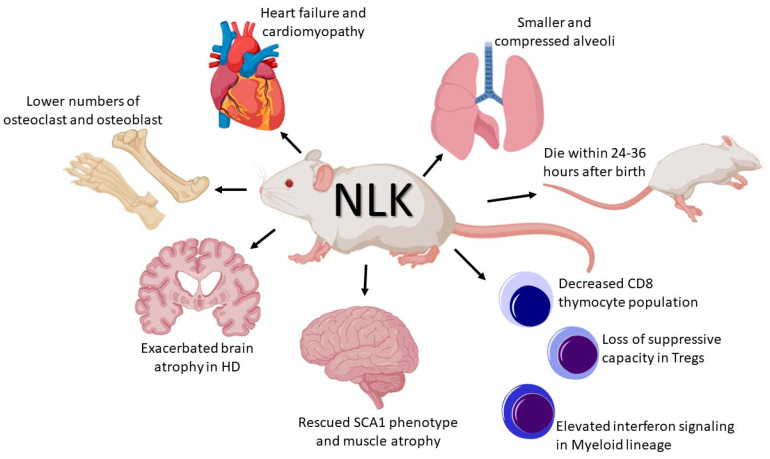
Figure 1.
Discoveries in the field of NLK signalling using mouse models. NLK is an evolutionary conserved MAP kinase known to be a negative regulator of the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway. Over recent years, mouse models targeting NLK have been established that have led to the discovery of NLK playing an important role in the function of organs including heart, lung, and skeleton. Additionally, multiple breakthroughs have been made showing that NLK regulates the function and differentiation of various immune cells. Finally, evidence has shown that NLK can regulate the phenotype seen in numerous neurodegenerative diseases. Representative summaries are given of major findings regarding the use of mouse models to study the function of NLK signalling. Images in the figure is taken from BioRender.com.