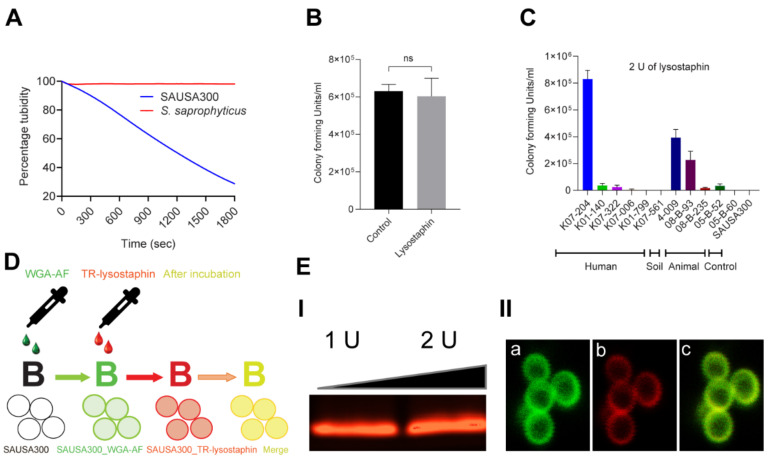
Figure 1.
Lysostaphin resistance pattern in ST72 isolates and the efficiency of lysostaphin binding to the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus. (A) Lysostaphin mediated killing kinetics of lysostaphin susceptible S. aureus USA300 (lyss) in comparison to the lysostaphin-resistant Staphylococcus saprophyticus (lysr) using the cell turbidity reduction assay. S. aureus USA300 (lyss) showed 70% reduction of cell turbidity compared to S. saprophyticus (lysr); (B) The lysostaphin resistance of S. saprophyticus (lysr) was further confirmed by colony forming unit (CFU) counting without (control) and with lysostaphin treatment, showing no significant difference in CFU counts; (C) Differential resistance pattern in 11 isolates of S. aureus ST72 against 2 U of lysostaphin upon 5 min of incubation wherein K07-204 (human), 4-009 (soil), and 08-B-93 (animal) showed lysostaphin resistance compared to lysostaphin-susceptible S. aureus USA300 (control); (D) Schematic diagram displays lysostaphin binding to the cell wall labeled with wheat germ agglutinin Alexa Fluor 488 (WGA-AF) (green fluorescence) with colocalized Texas Red labeled lysostaphin (red fluorescence of TR-lysostaphin); and (E) (I) Texas Red-labeled lysostaphin on agarose gel showing the red fluorescent protein band, (II) Colocalization of TR-lysostaphin on WGA-AF labeled green fluorescent cell wall of lysostaphin resistant human isolate of ST72 K07-204 wherein (a) the green channel of confocal photomicrograph shows WGA-AF labeled green fluorescent cell wall boundary of staphylococcal cell, (b) the red channel of the confocal photomicrograph shows the red fluorescent cell wall upon TR-lysostaphin binding, and (c) the merged channel of green (a) and red (b) shows the yellow fluorescent cell boundary, confirming the efficient binding of lysostaphin with the staphylococcal cell wall.