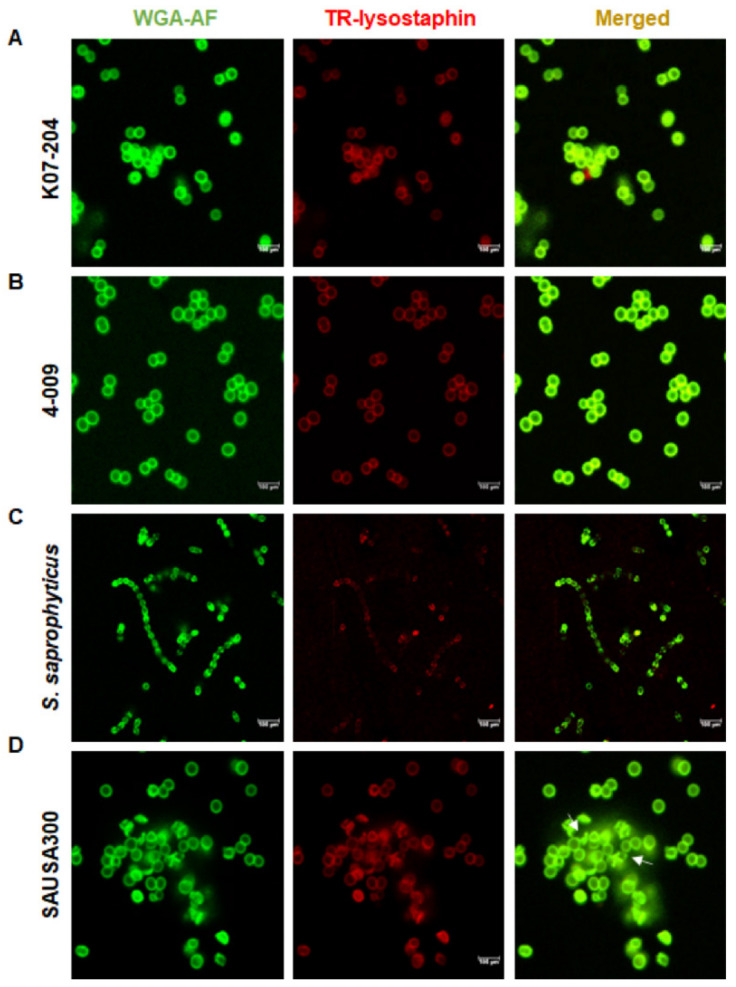
Figure 2.
Phenotypic assessment of the lysostaphin-binding and catalytic cleavage activity of lysostaphin resistant isolates of ST72. (A–D) Confocal microscopic images of lysostaphin-resistant ST72 human isolate K07-204 (A); lysostaphin-resistant ST72 soil isolate 4-009 (B); lysostaphin-resistant control S. saprophyticus (C); and lysostaphin-susceptible control S. aureus USA300 (D) upon treatment with TR-lysostaphin wherein white arrows indicate the broken cells after lysostaphin treatment. TR-lysostaphin binds efficiently with both ST72 isolates and S. aureus USA300, while TR-lysostaphin showed the least binding with S. saprophyticus.