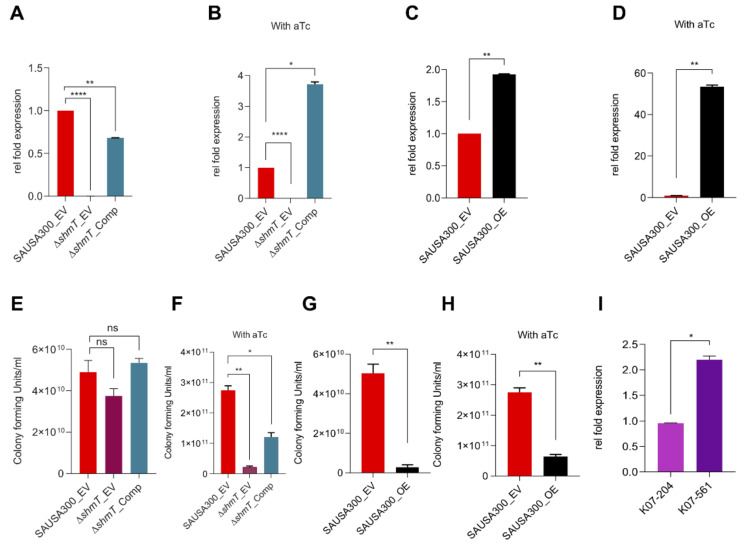
Figure 5.
Assessment of shmT expression and functional genomics to establish the role of shmT in lysostaphin resistance. (A–B) Gene expression of shmT in SAUSA300 recombinant strains including SAUSA300_EV, ΔshmT_EV and ΔshmT_Comp without induction (A), and with anhydrotetracycline (aTc) induction (B) wherein no transcript was detected in ΔshmT knockout with empty vector (ΔshmT_EV) as compared to the wild type S. aureus USA300 with empty vector (SAUSA300_EV) and ΔshmT complemented strain harboring pRMC2_shmT (ΔshmT_Comp). The shmT expression in (ΔshmT_Comp) strain was found to be moderate without aTc induction while it was significantly enhanced (3.5-fold) upon aTc induction. (C–D) Gene expression of shmT in SAUSA300 recombinant strains SAUSA300_EV and SAUSA300_OE constructed by expressing shmT in trans (plasmid: pRMC2_shmT) under tetracycline inducible promoter in the wild type S. aureus USA300. Expression of shmT in SAUSA300_OE versus SAUSA300_EV without (C) and with aTc induction (D) was found to be 2 and 53-fold higher, respectively, than control. (E–F) Assessment of colony forming unit in SAUSA300 recombinant strains SAUSA300_EV, ΔshmT_EV and ΔshmT_Comp showing the relative susceptibility of ΔshmT_EV strain compared to SAUSA300_EV and ΔshmT_Comp strains (E) whereas the susceptibility of ΔshmT_Comp strain was enhanced upon higher expression of shmT using aTc induction (F). The susceptibility of ΔshmT_EV showed the plausible involvement of shmT in lysostaphin resistance. (G–H) The SAUSA300_OE strain without induction (G), and with aTc induction (H) showed extreme susceptibility towards lysostaphin as compared to SAUSA300_EV. Both ΔshmT_Comp and SAUSA300_OE showed higher susceptibility to lysostaphin as compared to empty vector control SAUSA300_EV upon aTc induction and resultant overexpression of shmT; and (I) Expression of shmT in ST72 isolates K07-204 versus K07-561, wherein the K07-561 showed overexpression of shmT, which is the plausible reason of why K07-561 was susceptible to lysostaphin compared to K07-204.