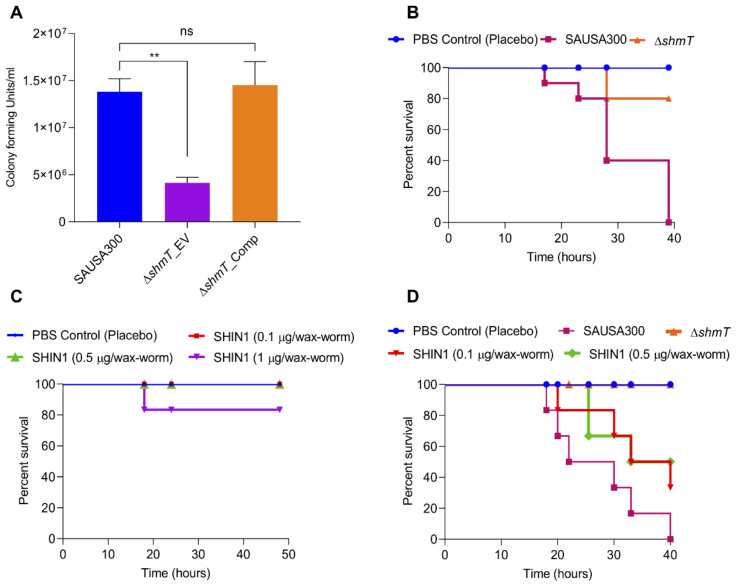
Figure 6.
Validating the role of shmT in virulence potential of SAUSA300 using in vitro mammalian cells, and in vivo wax-worm infection model. (A) Assessment of internalization (invasion/phagocytosis) and survival potential of SAUSA300, ΔshmT knockout and ΔshmT complemented strains under in vitro mammalian cell culture conditions using murine macrophage, RAW264.7 cells. The ΔshmT knockout showed significantly reduced survival inside the macrophage as compared to wild type SAUSA300 and ΔshmT complemented strains; (B) Survival graph for wax-worms infected by SAUSA300 and ΔshmT knockout (2.0 × 105 bacterial cells). The number of wax-worms in each group was 10 (n =10). (C) Assessment of toxicity of the SHMT inhibitor (SHIN1) for wax-worms (n = 10). Varying concentrations of SHIN1 (0.1 μg, 0.5 μg and 1μg in 20 μL solution) were injected into the wax-worms and the survival of the worms was observed for up to 80 h along with 20 μL placebo PBS control. The SHIN1 did not show any toxicity to the worms up to 0.5 μg; and (D) The treatment of SHIN1 inhibitor protected 50% wax-worm infected by the wild type SAUSA300, indicating that SHIN1 inhibits the pathogenesis of the wild type SAUSA300.