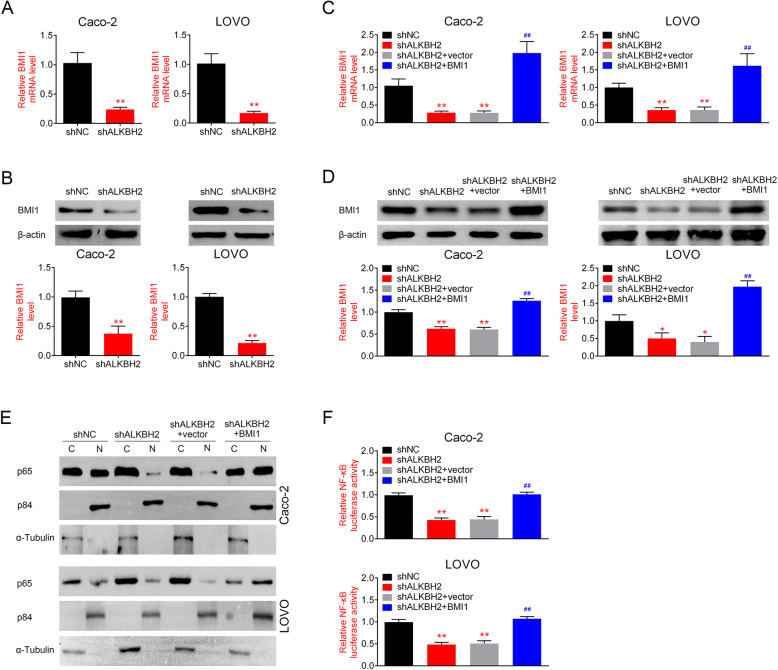
Fig. 4.
ALKBH2 regulates the expression of BMI1 and the downstream NF-κB pathway. a qRT-PCR was performed to determine the relative BMI1 mRNA expression in Caco-2 and LOVO cells transfected with sh-ALKBH2 or sh-NC, **P < 0.01 vs. sh-NC. BMI1 mRNA expression is significantly downregulated after ALKBH2 knockdown. b Western blotting was performed to assess the relative BMI1 protein expression in Caco-2 and LOVO cells transfected with sh-ALKBH2, sh-NC, or overexpression of BMI1, **P < 0.01 vs. sh-NC. Compared with the sh-NC group, the expression of BMI1 is downregulated in the sh-ALKBH2 group C. qRT-PCR was performed to measure the relative BMI1 mRNA expression in Caco-2 and LOVO cells after overexpression of BMI1**P < 0.01 vs. shALKBH2+vector. Downregulation of BMI1 is reversed by overexpression of BMI. d Western blotting was performed to quantify the relative BMI1 protein expression in Caco-2 and LOVO cells after overexpression of BMI1. **P < 0.01 vs. shALKBH2+vector. Downregulation of BMI1 is reversed by overexpression of BMI. e Western blotting was performed to assess the expression of p65 in the cytoplasm and nucleus. Nuclear protein p84 and α-Tubulin were used as nuclear and cytoplasmic marker, respectively, **P < 0.01 vs. sh-NC. C represents the cytoplasm and N represents the nucleus. Knockdown of ALKBH2 by shRNA decreases nuclear accumulation of the NF-κB p65 protein, whereas overexpression of BMI1 increases the content of NF-κB p65 protein in the nuclear component. f Immunofluorescent staining of subcellular localization of NF-κB (p65 subunit) in CRC cells, **P < 0.01 vs. sh-NC. The luciferase activities in sh-ALKBH2 treatment group show a significant reduction in nuclear p65, while BMI1overexpression leads to a prominent increase in nuclear p65