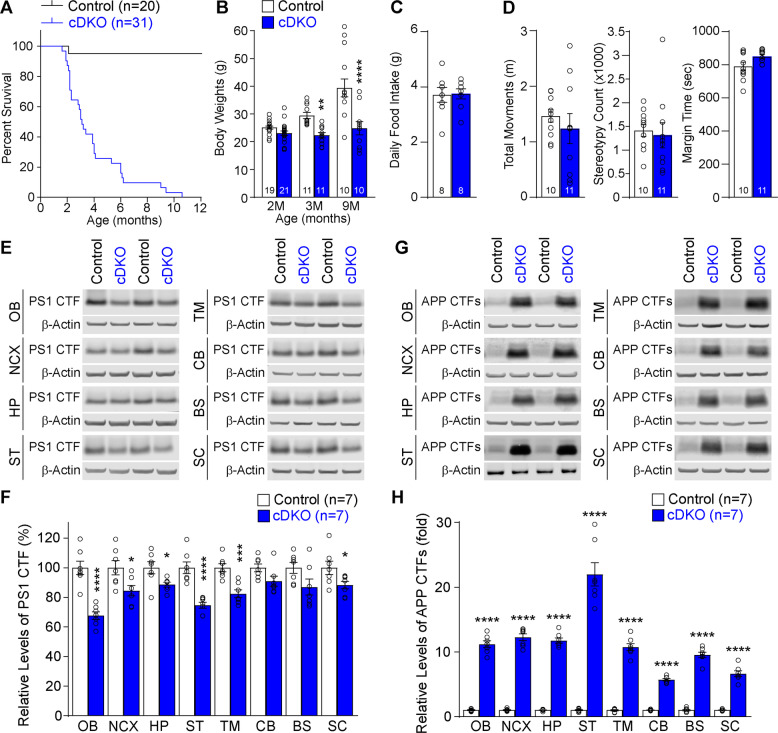
Fig. 1.
Reduction of PS1 levels and γ-secretase activity in the brain of IN-PS cDKO mice. a IN-PS cDKO mice exhibit dramatically earlier mortality as shown by the survival graph of IN-PS cDKO mice and littermate controls. Survival curves are plotted using the Kaplan-Meier method. b IN-PS cDKO mice fail to gain weight during aging, compared to littermate controls (F2, 76 = 9.69, p = 0.0002; 2 M: p = 0.68, 3 M: p = 0.0061, 9 M: p < 0.0001, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc comparisons). c Daily food intake of controls and IN-PS cDKO mice on chew diet at 2 months of age. Bar graph shows no significant difference in daily food intake amount between controls and IN-PS cDKO mice (p = 0.91, Student’s t-test). Daily food intake was calculated by averaging 7 days of food consumption per mouse. d During the open field test, IN-PS cDKO and control mice display similar total movements (p = 0.43, Student’s t-test), stereotypy count (p = 0.73), and the time spent of margin (p = 0.06) at 2 months of age. e Western blotting of total protein lysates from the dissected olfactory bulb (OB), neocortex (NCX), hippocampus (HP), striatum (ST), thalamus and midbrain (TM), cerebellum (CB), brain stem (BS), and spinal cord (SC) of control and IN-PS cDKO mice at 2 months of age. β-Actin was used as internal loading control. f Quantification analysis shows significant reduction of the PS1 CTF in the OB (p < 0.0001, Student’s t-test), NCX (p = 0.0230), HP (p = 0.0233), ST (p < 0.0001), TM (p = 0.0005), and SC (p = 0.0445) of IN-PS cDKO mice relative to littermate controls at the age of 2 months. The level of the PS1 CTF in the CB (p = 0.0577) and BS (p = 0.0704) of IN-PS cDKO mice is not statistically different from that of control mice. The value of the PS1 CTF in controls is set as 100%. g Western blotting of total protein lysates from the dissected olfactory bulb (OB), neocortex (NCX), hippocampus (HP), striatum (ST), thalamus and midbrain (TM), cerebellum (CB), brain stem (BS), and spinal cord (SC) of the controls and IN-PS cDKO mice at 2 months of age shows dramatic increases of APP CTFs in IN-PS cDKO mice. β-Actin was used as internal loading control. h Quantification analysis shows accumulation of APP CTFs in various brain sub-regions of IN-PS cDKO relative to controls at the age of 2 months (p < 0.0001, Student’s t-test). The value of APP CTFs in controls is set as 1. All data represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. The value in the column indicates the number of mice used in each experiment