Fig. 8.
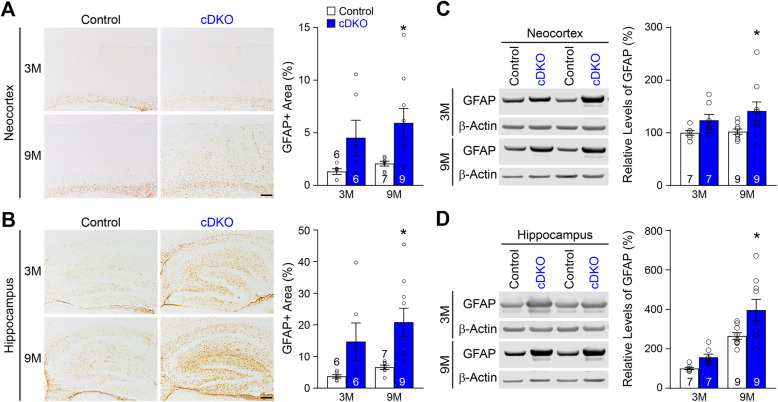
Progressive astrogliosis in the cerebral cortex of IN-PS cDKO mice. a Left: GFAP immunostaining of comparable sagittal sections in the neocortex of IN-PS cDKO and littermate control brains at 3 and 9 months of age. Right: Stereological quantification shows significant age-dependent increases in the percentage of GFAP-immunoreactive areas in the neocortex of IN-PS cDKO mice relative to control mice (F1, 24 = 0.08, p = 0.79; 3 M: Control 1.31 ± 0.27%, cDKO 4.53 ± 1.67%, p = 0.17; 9 M: Control 2.07 ± 0.22%, cDKO 5.93 ± 1.39%, p = 0.0399, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc comparisons). b Left: GFAP immunostaining of comparable sagittal sections in the hippocampus of IN-PS cDKO and littermate control brains at 3 and 9 months of age. Right: Stereological quantification shows significant age-dependent increases in the percentage of GFAP-immunoreactive areas in the hippocampus of IN-PS cDKO mice relative to control mice (F1, 24 = 0.17, p = 0.68; 3 M: Control 3.71 ± 0.53%, cDKO 14.69 ± 5.90%, p = 0.15; 9 M: Control 6.57 ± 0.69%, cDKO 20.81 ± 4.46%, p = 0.0214, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc comparisons). c Left: Increased GFAP levels in the neocortex of IN-PS cDKO mice. Western blotting of total protein lysates from the neocortex of IN-PS cDKO mice and littermate controls at 3 and 9 months of age. β-actin was used internal loading control. Right: Quantitative analysis shows significant age-dependent increases of GFAP levels in the neocortex (F1, 28 = 0.41, p = 0.52; 3 M: p = 0.36, 9 M: p = 0.0341, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc comparisons) of IN-PS cDKO relative to controls. The value of GFAP in littermate controls is set as 100%. d Left: Increased GFAP levels in the hippocampus of IN-PS cDKO mice. Western blotting of total protein lysates from the dissected hippocampus of IN-PS cDKO mice and littermate controls at 3 and 9 months of age. β-actin was used as internal loading control. Right: Quantitative analysis shows significant age-dependent increases of GFAP levels in the hippocampus (F1, 28 = 1.30, p = 0.26; 3 M: p = 0.53, 9 M: p = 0.0108, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc comparisons) of IN-PS cDKO relative to controls. The value of GFAP in littermate controls is set as 100%. Scale bar: 100 μm. All data represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05. The value in the column indicates the number of mice used in each experiment