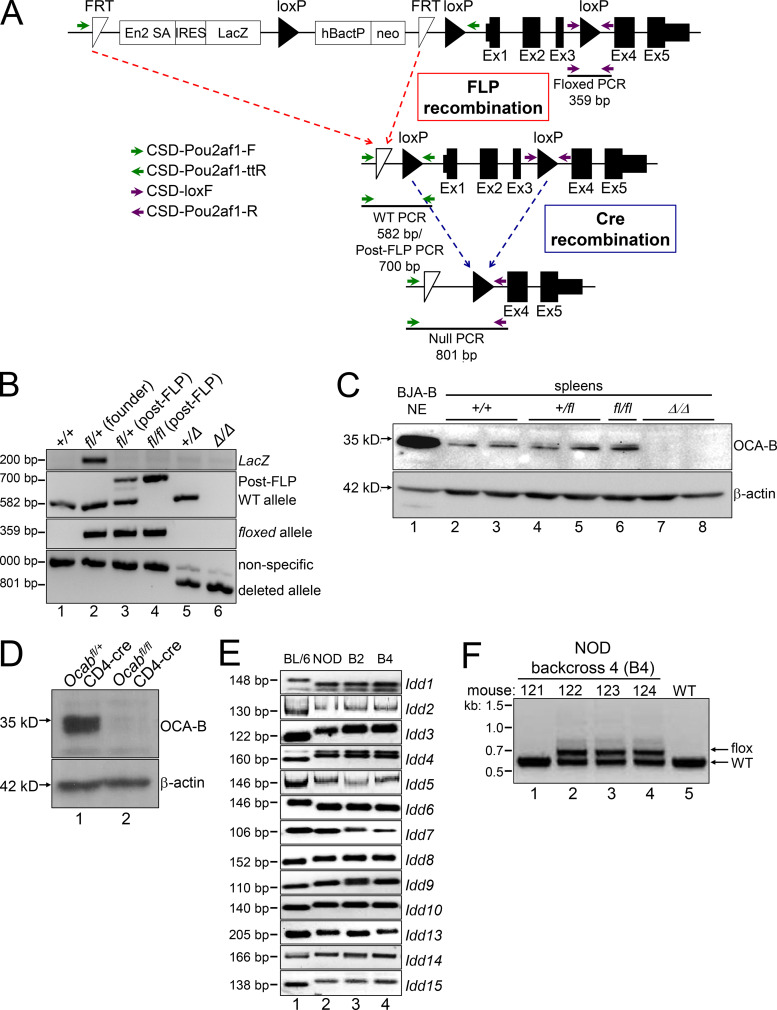
Figure S1.
Ocab (Pou2af1) conditional allele. (A) Targeting event. Crossing with FLPRosa26 results in conditional (fl) allele. Primer pairs used for genotyping are depicted with arrows. FRT, flippase recognition target. (B) Example genotyping of the targeted allele and recombination events. The founder animal is in lane 2. The primer pairs shown in A were used. (C) OCA-B immunoblots from spleens of control, fl/fl, and Δ/Δ animals. BJA-B B cell nuclear extract is shown as a positive control (lane 1). (D) The Ocab (Pou2af1) conditional allele was crossed to CD4-cre. Total splenic CD4+ T cells were isolated from an Ocabfl/flCD4-cre animal or a Ocab+/flCD4-cre littermate control, and stimulated for 2 d in vitro using plate-bound CD3ε and soluble CD28 antibodies. An OCA-B immunoblot of stimulated total T cells is shown. β-Actin is shown as a loading control. (E) To generate NOD.Ocab conditional mice by speed congenic backcross, microsatellite repeat polymorphisms at the Idd loci were tested by PCR using the primers in Table S1. Backcross generations 2 and 4 (B2 and B4) are shown (lanes 3 and 4), together with parent C57BL/6 (lane 1) and target NOD (lane 2) genomic DNA as controls. Images are of different PCR products resolved using agarose or PAGE. (F) Example genotyping of Ocab WT and conditional alleles in B4 backcrossed mice. An agarose gel image is shown. Mouse 122 corresponds to the B4 animal shown in B and was used as the founder animal. This animal was crossed with NOD.CD4-cre for subsequent experiments with the conditional allele.