Figure 2.
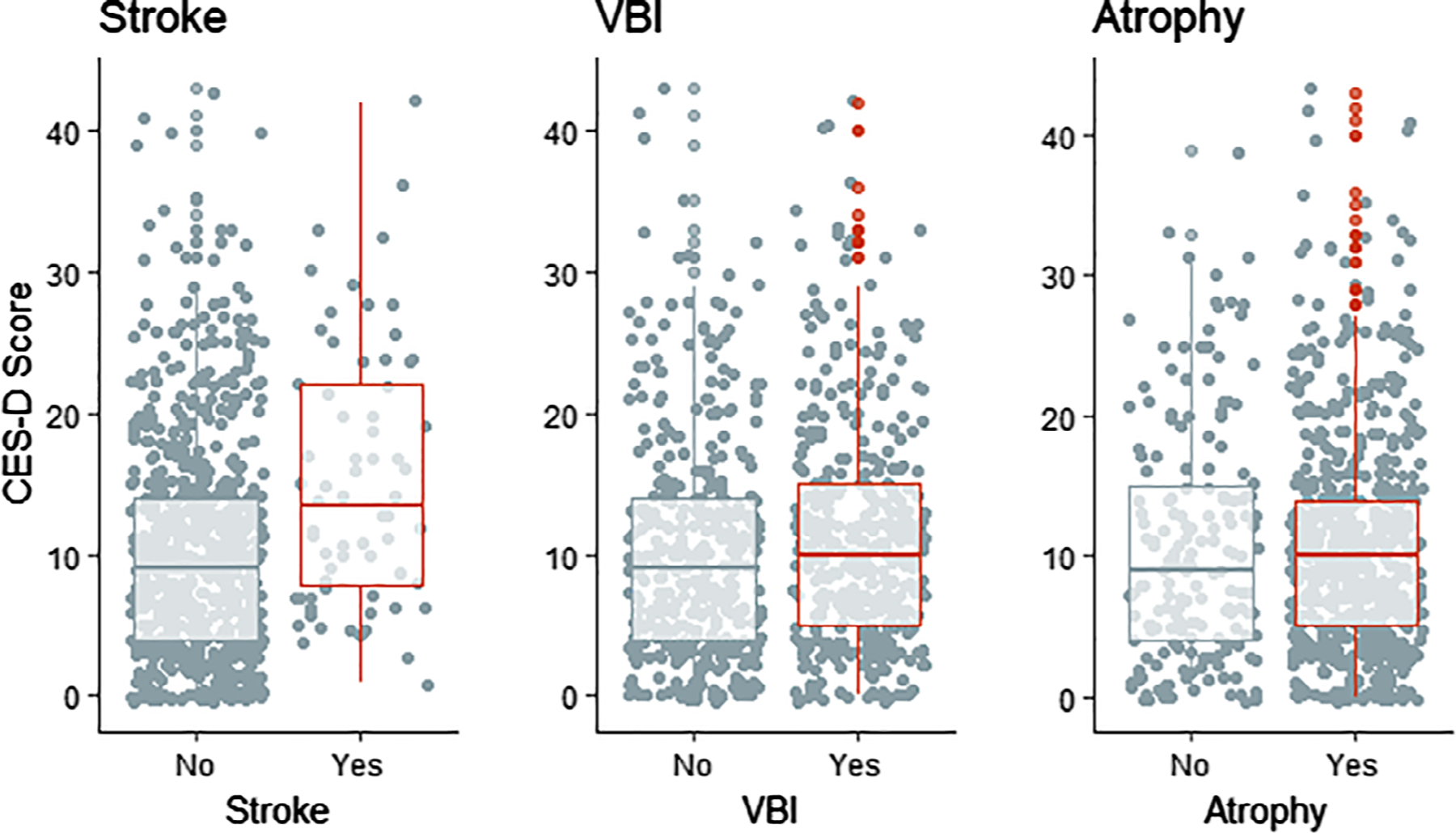
Scatter and box plots comparing Centers for Epidemiologic Studies Depression (CES-D) scores (Y-axes) for participants with (red) and without stroke (left), vascular brain injury (VBI; center), or cerebral atrophy (right) in older American Indians (2010–2013). VBI is defined as the presence of infarcts, hemorrhages, or white matter disease. Atrophy is defined as sulcal dilatation or ventricle enlargement. One-way analysis of variance testing for differences in variation in CES-D scores between groups for stroke, VBI, and atrophy detected P values <.001, .136, and .631, respectively.
