Figure 2.
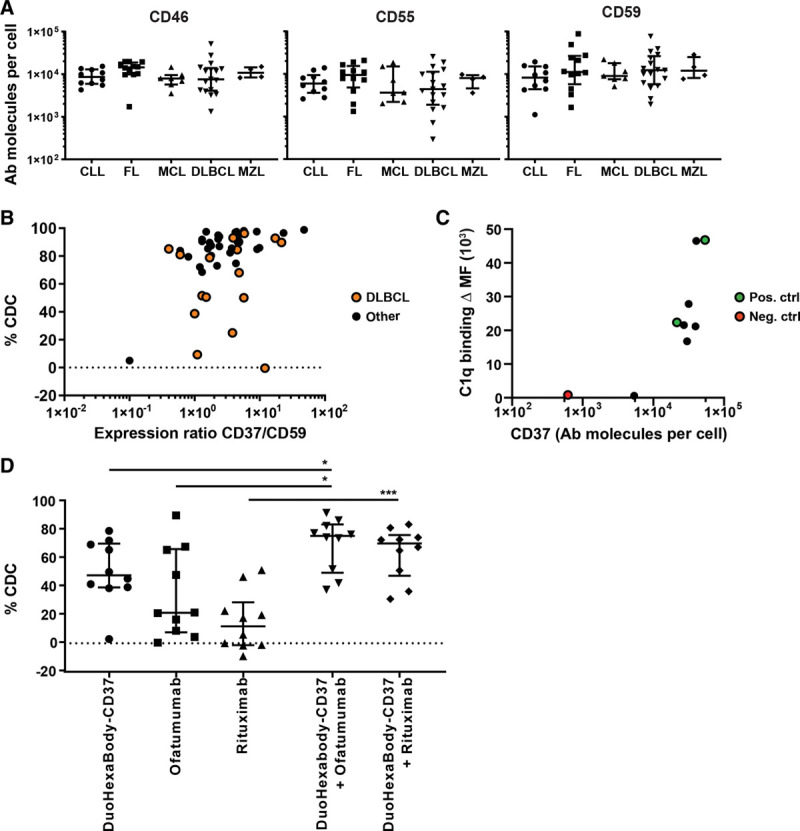
Low sensitivity to DuoHexaBody-CD37–mediated CDC is not associated with expression of CD37 and CRPs and can be improved by combination with CD20 mAbs. A, Quantified expression levels (antibody molecules per cell) of complement regulatory proteins CD46, CD55, and CD59 on tumor B-cells in specific B-cell malignancy subtypes; CLL (n = 10), FL (n = 12), MCL (n = 7), DLBCL (n = 18), and MZL (n = 4) (ns; nonparametric Kruskal-Wallis test). Data shown are CDC in individual patient samples, in addition to the median and interquartile range. B, CDC activity of DuoHexaBody-CD37 (10 μg/mL) correlated with the ratio of CD37/CD59 expression levels for all B-cell malignancy subtypes grouped together, for DLBCL patient samples specifically (•) and for B-cell malignancy subtypes other than DLBCL (Spearman’s correlation r = 0.4423, **P = 0.0013; r = 0.2843, P = 0.2678; and r = 0.5158, **P = 0.0025, respectively). Data are shown relative to a no antibody control sample. C, Expression levels of CD37 (antibody molecules per cell) correlated with C1q binding (ΔMFI) for 6 samples with low CDC response (CDC < 60%) (•), 1 CD37-negative sample as negative control (•) and 2 high responding samples as positive control (•) (Spearman’s correlation r = 0.7833, *P = 0.0172). D, CDC induced by a combination of DuoHexaBody-CD37 and rituximab or ofatumumab (10 μg/mL + 10 μg/mL) vs single antibody (10 μg/mL) (n = 10) (*P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001; Friedman test with Dunn multiple comparison test) relative to a no antibody control sample. All data are shown as the median and interquartile range. CDC = complement-dependent cytotoxicity, CLL = chronic lymphocytic leukemia, CRP = complement regulatory protein, DLBCL = diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, FL = follicular lymphoma, mAbs = monoclonal antibodies, MCL = mantle cell lymphoma, MFI = median fluorescence intensity, MZL = marginal zone lymphoma.
