Figure 7.
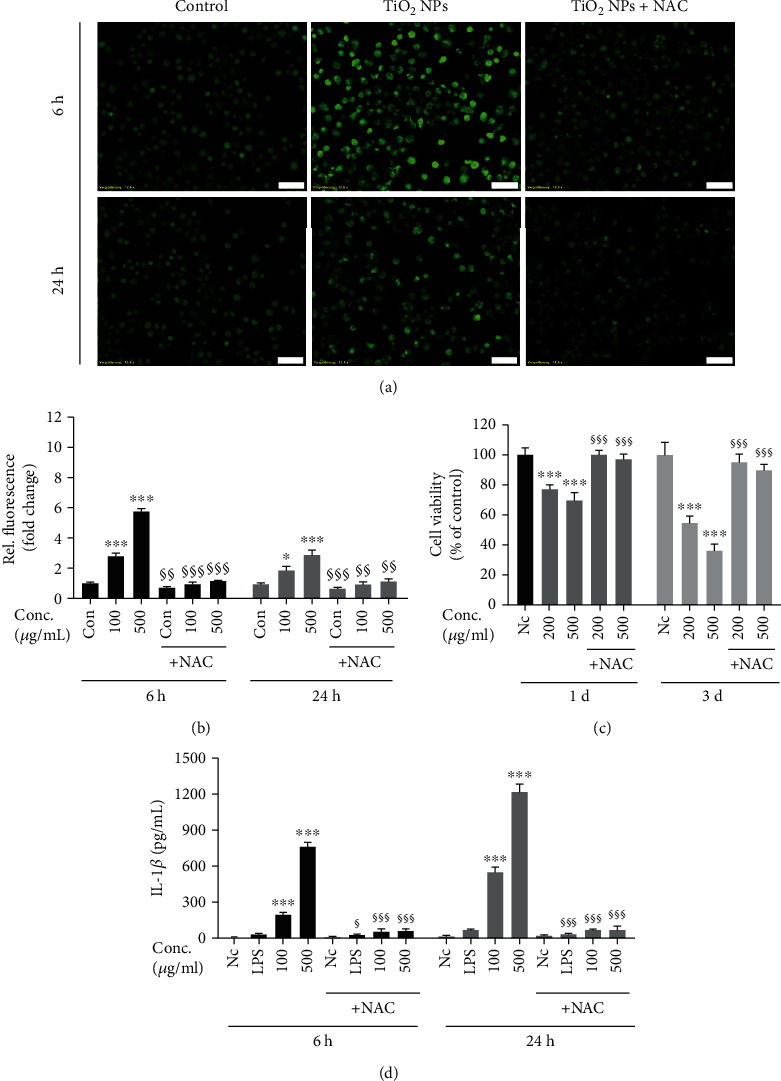
Protective role of ROS scavenger (NAC) on TiO2 NP-induced cell death and IL-1β release. LPS-primed macrophages were preincubated for 30min with/without NAC (5mM), and then cotreated with TiO2 NPs at the indicated doses for 6 and 24h. (a) Following exposure, cells were incubated with DCFH-DA (20μM) for 30 min at 37°C, and ROS production was detected by fluorescence microscopy (20x). Scale bar: 50μm. (b) Relative quantification of ROS generation (fold change). The protective role of NAC on (c) cell viability and release of (d) IL-1β were measured by CCK-8 and ELISA, respectively. Data are presented as mean + SD of three identical experiments performed in three replicates. ∗ indicates significant difference as compared to the control (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001); § indicates significant inhibitory effect of NAC on cell death and proinflammatory cytokine generation (§p < 0.05, §§p < 0.01, and §§§p < 0.001).
