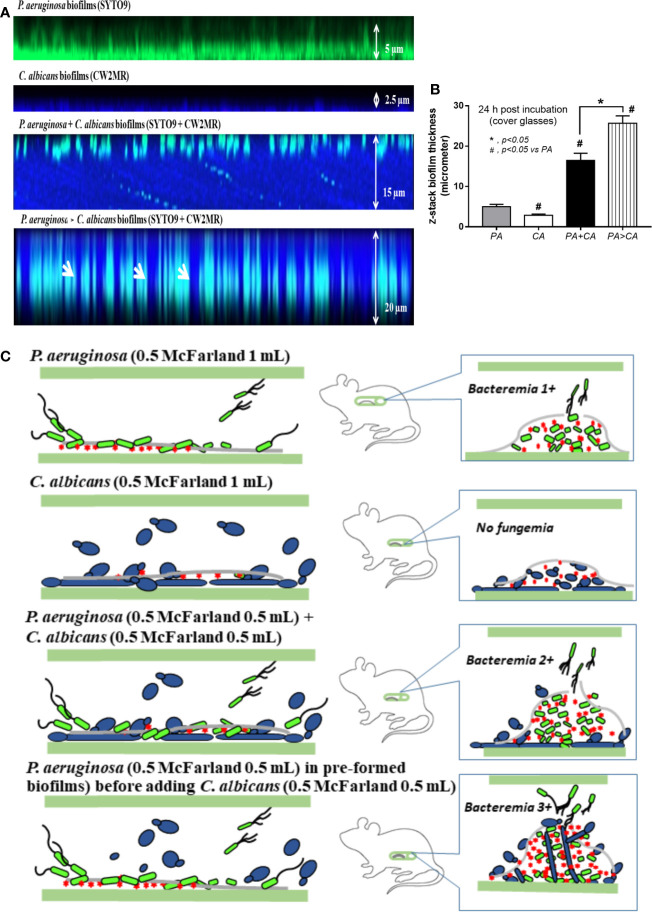
Figure 12.
Representative fluorescent z-stack lateral-view images of bacterial nucleic acid by SYTO9 (green) and fungal cell wall by calcofluor white (CW2MR; blue) from biofilms of single (P. aeruginosa or C. albicans) and mixed organisms that initially incubated together and incubated for 24 h (P. aeruginosa + C. albicans) or the Candida addition at 12 h biofilm-formed bacteria (P. aeruginosa > C. albicans) and further incubated for another 12 h on cover glasses (A) is demonstrated (arrows indicate the possible Candida germ tubes that grow from the top into the bottom of biofilms). In addition, thickness of the biofilms (B) and the working hypothesis (left side, catheter during the preparation; right side, the proposed situations in catheter biofilms in vivo) show the enhanced bacterial dissemination in P. aeruginosa > C. albicans biofilms from Candida germ-tube elongation (C) are demonstrated. Mean ± SE was used for data presentation, and the differences between groups were examined by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s analysis for comparisons of multiple groups or 2 groups (B). A p-value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. (Independent triplicate experiments were performed for A, B.)