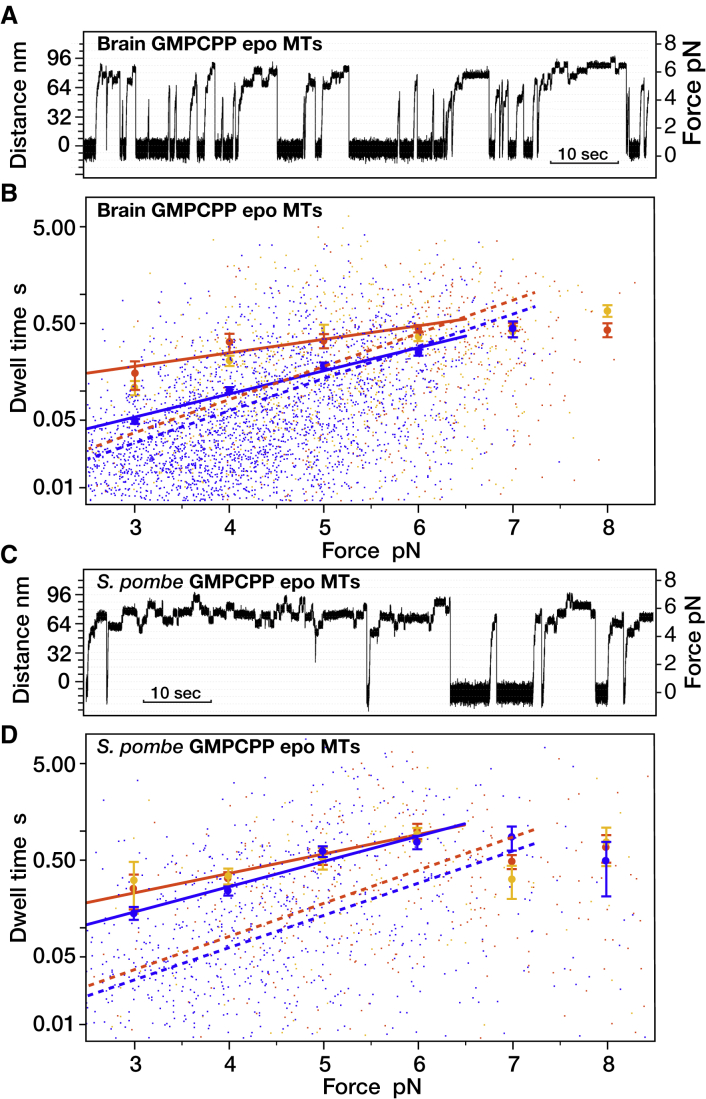
Figure 2.
Mechanics of kinesin stepping under load on different MT types. (A and C) Optical trapping position versus time traces show the much shorter stalls typically seen with brain GMPCPP epothilone MTs (A) compared with S. pombe GMPCPP epothilone MTs (C). (B and D) Dwell times versus load for kinesin stepping on (B) brain GMPCPP epothilone MTs and (D) S. pombe GMPCPP epothilone MTs. As in Fig. 1C, dwell times depend exponentially on load, mean forward-step dwell times are characteristically shorter than mean backstep or detachment dwell times, and mean backstep and detachment dwell times are indistinguishable. Approaching stall force, backstep dwell times reach a plateau, above which further increases in hindering load have little effect on dwell time (15). Mean dwell times in the region below stall force were fitted using log(y) = kx + b. Parameters are as follows: (B) blue, k = 0.53, b = −4.4; orange, k = 0.25, b = −2.3; (D) blue, k = 0.6, b = −3.6; orange, k = 0.46, b = −2.7. Errors are mean ± SE. In (B) and (D), fits for GDP Taxol MTs are shown for comparison (dotted lines). To see this figure in color, go online.