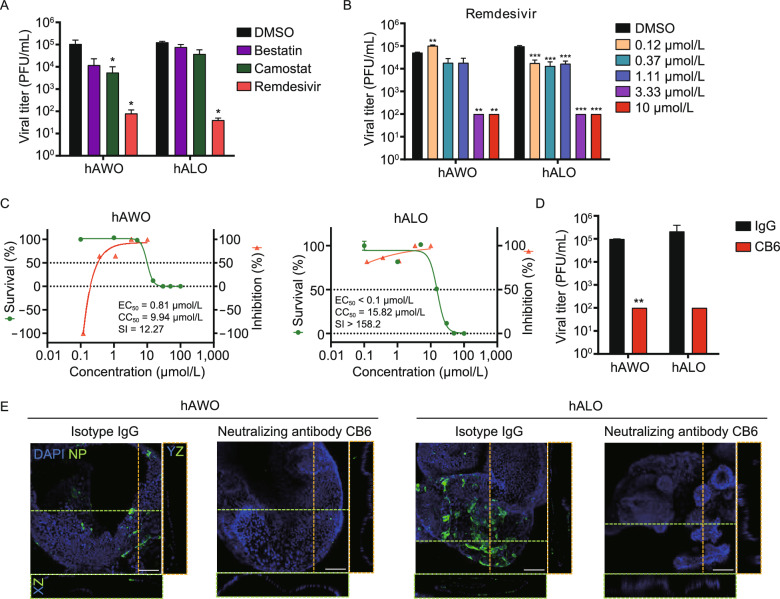
Figure 6.
Remdesivir and a human neutralizing antibody inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication in lung organoids. (A) hAWOs and hALOs were infected with SARS-CoV-2, the indicated compounds were added into the culture media 2 h after infection. 48 h later, the virus titers were determined by plaque assay with Vero E6 cells. *P < 0.05, by one-way ANOVA analysis. (B) Virus infected hAWOs and hALOs were treated with remdesivir at indicated concentrations for 48 h. The virus titers were determined by plaque assay. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, by one-way ANOVA analysis. (C) Inhibition and toxicity curves of remdesivir in hAWOs and hALOs. Inhibition and cytotoxicity of remdesivir was quantified by viral titers and viable cell counting, respectively. The left and right Y-axis of these graphs represent mean survival of the cells and inhibition of virus titers, respectively. Bars represent mean ± SD, n = 3. (D and E) hAWOs and hALOs were infected with SARS-CoV-2 at the present of a human neutralizing antibody CB6 or isotype IgG, and virus titers were detected at 48 hpi. **P < 0.01, by unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t test (D). Whole-mount staining of hAWOs and hALOs. Nucleoprotein (NP) was stained to visualize infected cells. The XZ and YZ planes of the horizontal and vertical cut view of Z-stack images are shown at the bottom and right, respectively (E). Scale bars: 100 µm