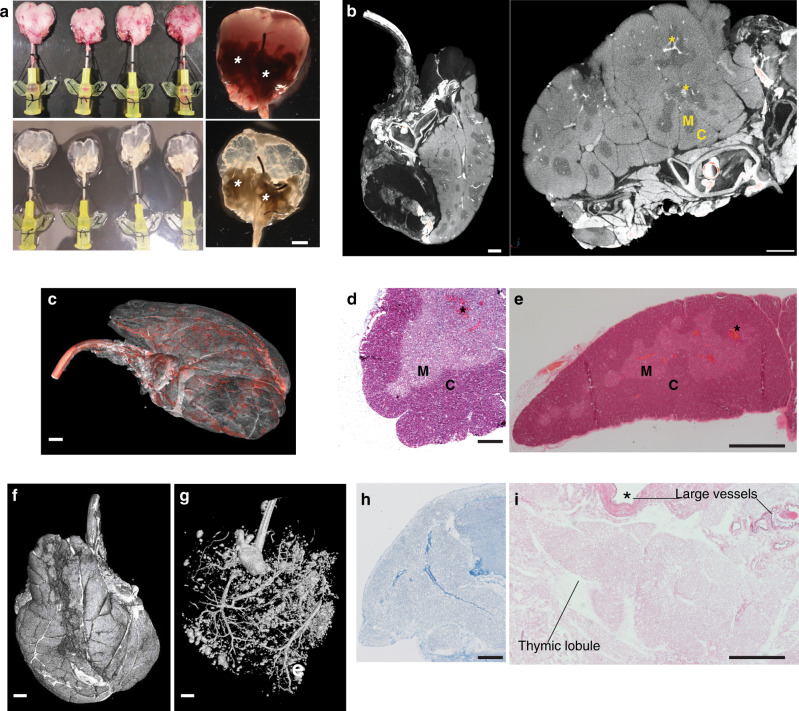
Fig. 4. Whole-organ thymus perfusion and decellularisation.
a Gross appearance of cannulated rat thymi before (upper panels) and after (lower panels) decellularisation. A 24G cannula is inserted into the carotid artery and used to perfuse the organ with detergent and enzymatic solutions. Asterisks indicate extra-thymic tissues that allowed connection between thymic tissue and cannula through the large blood vessels (n = 120). Scale bar, 2 mm. b Micro-CT images of cannulated rat thymus showing extra-thymic tissues, large blood vessels and the 24G cannula entering the artery. Iodine contrast shows clear demarcation between cortex (C, bright) and medullary (M) areas; blood vessels (asterisks) are represented by very bright areas between and inside the parenchyma (n = 3). Scale bar, 1.5 mm. c Micro-CT 3D image of whole rat thymus cannulated where iodine contrast shows vasculature tree (segmented in red, n = 2). Scale bar, 1.2 mm. d Masson’s trichrome stain of a fresh rat thymus lobe staining in red keratins, in blue collagen and in pink cytoplasm. C cortex, M medulla (n = 3 thymi). Scale bar, 250 μm. e Haematoxylin & Eosin (H&E) stain of a fresh rat thymus. C cortex, M medulla (n = 3 thymi). Scale bar, 500 μm. f Micro-CT image of cannulated rat thymus showing the whole 2 lobes in 3D. Scale bar, 1.2 mm. g Micro-CT image of a cannulated rat thymus injected with Microfil® and thresholded to demonstrate perfusion of both thymic lobes. Scale bar, 1.2 mm. h Masson’s trichrome stain of a paraffin section of a decellularised rat thymus scaffold demonstrating collagen fibres (blue) and absence of keratins, muscle fibres and cell cytoplasm (n = 3 scaffolds). Scale bar, 250 μm. i H&E of a decellularised thymus scaffold showing intact thymic lobule ECM and preservation of both large and small vasculature wall (n = 4 scaffolds). Scale bar, 500 μm.