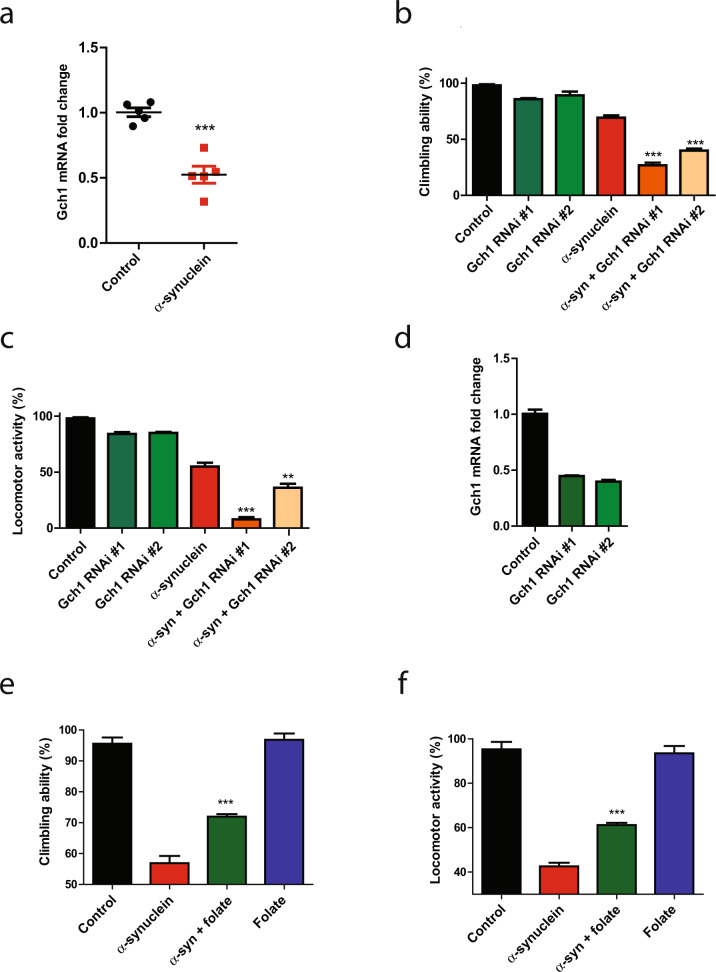
Fig. 4. Gch1 and folate control α-synuclein toxicity.
a Quantitative RT-PCR analysis shows decreased Gch1 expression in human α-synuclein transgenic flies at 10 days of age when compared to control flies. Neuronal knockdown of Gch1 enhances α-synuclein induced (b) climbing and (c) locomotor activity deficits when compared to flies expressing α-synuclein alone. d Quantitative RT-PCR analysis shows the knockdown level of Gch1 in the two RNAi lines used. Dietary folate supplementation in flies partially rescues α-synuclein induced (e) climbing and (f) locomotor activity deficits when compared to flies expressing α-synuclein not receiving folate. Control genotype: nSyb-QF2, nSyb-GAL4/+. All data are represented as mean ± SEM. For more than two groups, data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc test for multiple groups. For two groups, data are analyzed using two-tailed student’s t test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005, n = 6. Flies are 10 days old in a–c and e, f, and 1 day old in d.