Figure 2.
Strategy for AN13762 Target Deconvolution
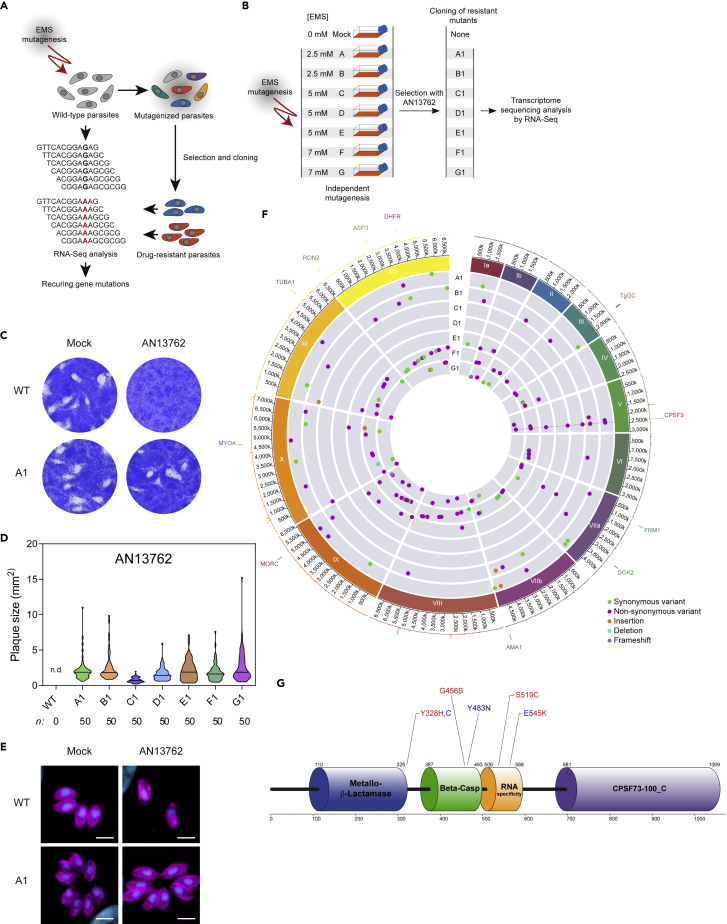
(A) Diagram of key steps of the forward genetic screen to map mutations conferring drug resistance in T. gondii parasites. EMS-mutagenized population of T. gondii tachyzoites was selected in the presence of a lethal concentration of AN13762 to isolate drug-resistant parasites. Analysis of the parental wild-type strain and multiple resistant clones by variant-calling of sequencing reads generated by RNA-seq to identify EMS-induced mutations in coding sequences conferring drug resistance.
(B) Schematic of the strategy used to obtain T. gondii-resistant parasites to AN13762. From each mutagenesis experiment a single clone (A1 to F1) was isolated and analyzed by RNA-seq.
(C) AN13762-resistant parasites form plaques after 7 days of growth in the presence of 10 μM AN13762. Complete dataset in shown in Figure S2A.
(D) Quantification of plaque sizes of wild-type parasites and resistant lines (A1 to G1) when cultured in the presence of AN13762. n.d., not detected. Associated data are shown in Figure S2C.
(E) Fluorescence microscopy showing intracellular growth of T. gondii AN13762-resistant lines. HFF cells were infected by the indicated T. gondii strains in the presence or absence of 10 μM AN13762. At 24 h post-infection, cells were fixed and stained with antibodies against GAP45 (magenta) and Hoechst (blue) to detect the inner membrane complex (IMC) of parasites and nuclei, respectively.
(F) Circos plot summarizing single nucleotide variants (SNVs), insertions, and deletions detected by transcriptomic analysis of the T. gondii AN13762-resistant lines, grouped by chromosome (numbered in Roman numerals with size intervals given outside). Each dot in the seven innermost gray tracks corresponds to a scatterplot of the mutations identified in the coding regions of the seven drug-resistant strains, with each ring representing one of the seven drug-resistant lines (A1 to G1). In the second outermost track, lines depicting whole-genome RNA-seq data of the T. gondii parental strain (RPKM values of genes are shown). Each bar in the outermost track represents locations of selected archetypal essential genes. See Table S2 and Figure S4 for transcriptomic analysis.
(G) TgCPSF3 domain architecture as predicted from PFAM databases and crystal structures of Cryptosporidium CPSF3 (Swale et al., 2019). Positioning of residues that were mutated in parasites resistant to AN13762 (Y328H, G465S, S519C, and E545K, in red) or AN3661 (Y328C, Y483N, and E545K, in blue) are indicated.