Figure 4.
Docking Studies for Chemotypes AN13762 and AN3661
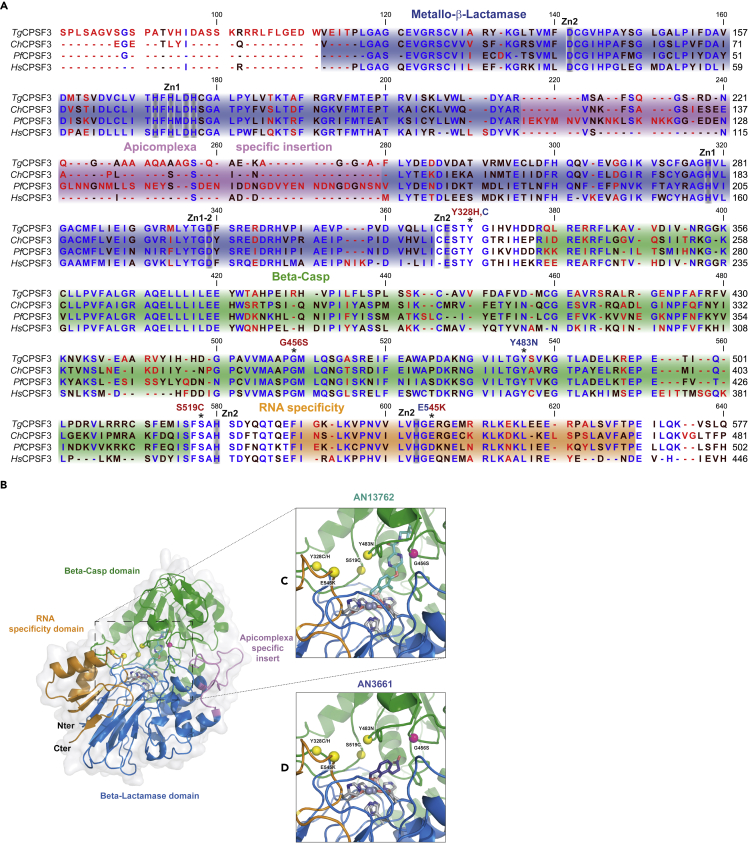
(A) Multiple sequence alignment of CPSF3 proteins from T. gondii (Tg), C. hominis (Ch), P. falciparum (Pf), and CPSF73 of H. sapiens (Hs). The domain architecture is indicated as follows: blue, metallo-β-lactamase; green, β-CASP; orange, RNA specificity domain; magenta, the insertion within the MBL domain of apicomplexan parasites. Residues mutated in drug-resistant parasites are indicated by asterisks. The highly conserved residues involved in the coordination the zinc atoms Zn1 or Zn2 are indicated in gray. Mutations identified in parasites resistant to AN13762 or AN3661 are indicated in red and blue text, respectively.
(B) Schematic of Cryptosporidium hominis CPSF3/AN3661 co-crystal structure and modeling with AN13762. CPSF3 is displayed in a cartoon fashion with the same domain color code as in (A) surrounded by a light gray surface representation. Catalytic zinc atoms and coordinating residues are shown in gray sticks, whereas resistant mutations are shown in yellow and pink spheres.
(C) Zoom into the catalytic pocket with AN13762 manually placed colored in cyan.
(D) Zoom into the catalytic pocket binding AN3661 colored in dark purple.