Figure 5.
Efficacy Against C. parvum in Cell Culture and Neonatal Mouse Model
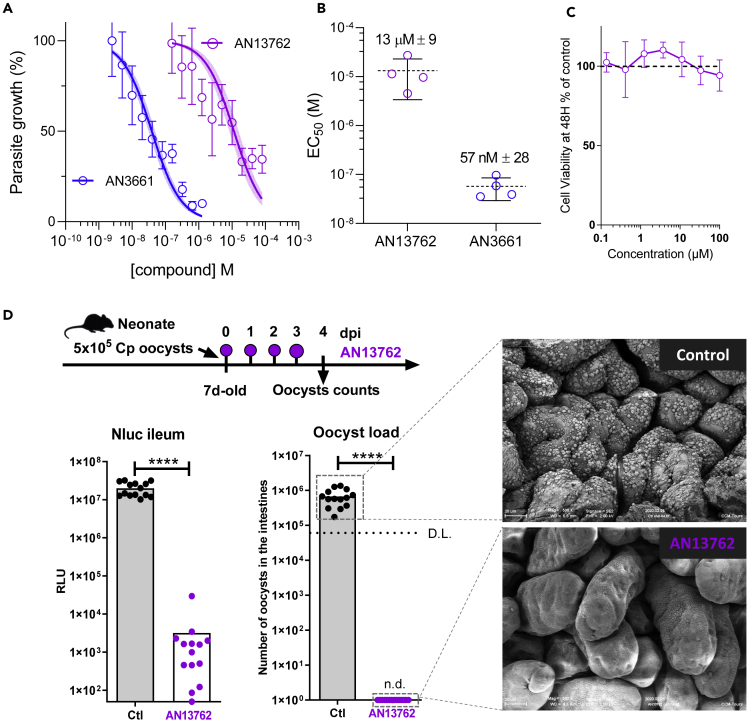
(A) Comparative inhibitory activity of AN13762 and AN3661 against C. parvum INRAE Nluc strain in human ileocecal HCT-8 cells. The effect of both drugs in reducing parasitic load in epithelial cells was monitored by the luminescence signal of transgenic Nluc parasites (each concentration point represents the average of six measurements ±SD.) Curves corresponding to AN13762 and AN3661 are in magenta and blue, respectively. Corresponding fluorescence microscopy images showing intracellular growth of C. parvum parasites can be found in Figure S5.
(B) Calculated EC50 measurements are shown for AN13762 and AN3661 (n = 4 for each drug). Mean EC50 values ±SD from 4 independent biological replicates are indicated.
(C) HCT-8 cell viability assay performed 48 h with increasing concentration of AN13762. Percent viability compared with the untreated control is displayed as a function of compound concentration in micromolar concentrations. Data are presented as mean ± SD of at least two independent biological assays. Dotted line represents 100% viability.
(D) Schematic representation of the 4-day oral dosage of AN13762 (40 mg/kg) in CMC from day 0 (4 h post-infection) in 7-day-old neonatal mice previously infected with 5 × 105 oocysts. The degree of infection was monitored by counting the oocysts in the small intestine of the animals at 4 dpi (D.L., detection limit = 6 × 104 oocysts/intestine) and by monitoring Nluc activity on a small piece of ileum of each neonatal mouse (n = 14 animals per group). n.d., not detected. Mann-Whitney test, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001. Scanning electron microscopic imaging of neonatal mice ileum was performed at the end of the experiment on treated (AN13762) and mock treated (control) animals.