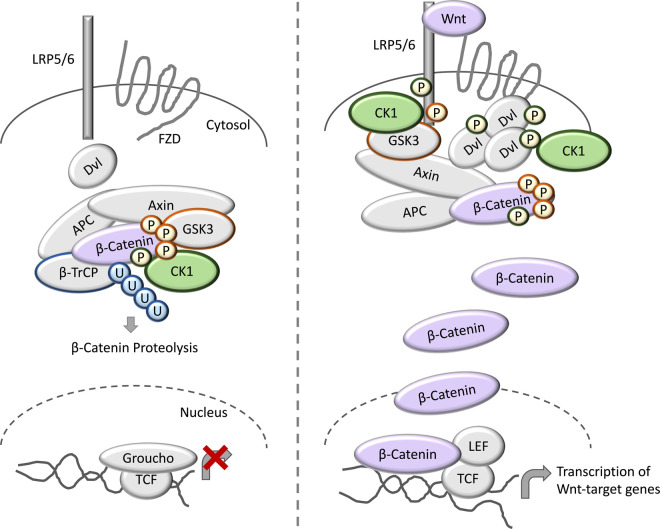
Figure 3. CK1 in Wnt signalling.
In the absence of Wnt ligands, β-catenin is held by the so-called destruction complex composed of Axin, APC, the E3 ubiquitin ligase substrate receptor β-TrCP, and the kinases CK1 and GSK3. Sequential phosphorylation of β-catenin by CK1 and GSK3 triggers β-catenin ubiquitination by the β-TrCP-complex, and its subsequent proteasomal degradation. In the nucleus, Groucho binds TCF to block the transcription of Wnt target genes. Following binding of Wnt ligands to the receptors LRP5/6 and FZD, LRP5/6 becomes phosphorylated, and triggers the formation of the Wnt signalosome, largely composed of Axin and Dvl. This recruits the destruction complex to the membrane. β-catenin is stabilised in the cytosol and is free to enter the nucleus where it displaces Groucho from TCF, and together with LEF, activates transcription of Wnt target genes. CK1 has also been reported to phosphorylate the LRP5/6 and Dvl in the presence of Wnt ligands.