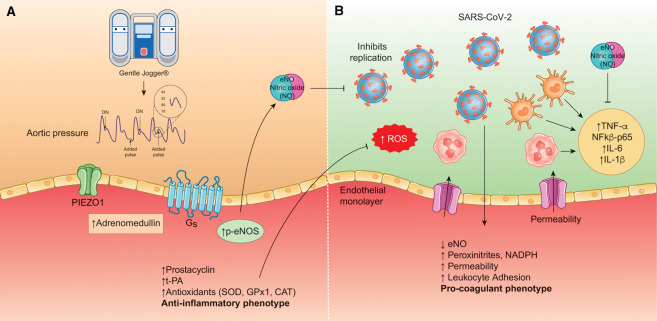
Figure 1.
A model of pulsatile shear stress (PSS) effects on a normal (A) and SARS-CoV-2-activated (B) endothelial monolayer. The left side of the diagram (A) depicts a normal endothelial cell monolayer. Gentle Jogger (Jogging Device) induces added pulses to the normal circulation [9]. The dichrotic notch (DN) for each aortic pulse waveform is shown along with the added pulsations induced by Gentle Jogger. Pulsations derived from the normal circulation and those produced by the Gentle Jogger, produce PSS on the vascular endothelium monolayer which activates the cation channel PIEZO1. The latter increases production of adrenomedullin, which via an intermediary step (activates the heterotrimeric G protein (Gs) receptor, leading to activation of protein kinase A(PKA) which activates eNOS by phosphorylation, thus increasing endothelial-derived nitric xide (eNO) [10]. PSS, increases prostacyclin, tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), antioxidants (superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase 1 (GPx1), catalase (CAT)) and produces an anti-inflammatory endothelium phenotype. The right side (B) depicts an activated endothelium from SARS-CoV-2, in which the endothelium monolayer loses its barrier function with increased permeability, reactive oxygen species (ROS) peroxinitrites and NADPH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) are produced, and the endothelial cell manifests a pro-coagulant phenotype. Bioavailability of nitric oxide is decreased. Additionally, neutrophils and macrophages are stimulated by the virus to produce an increase in the following cytokines; tumor necrosis alpha (TNF-α), nuclear translocation of the NF-kβ-p-65 (nuclear factor kappa beta), and interleukin 6 (IL-6), interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β) and ROS. eNO produced by PSS, inhibits replication of the virus and decreases the production of cytokines. PSS is a means to widely distribute beneficial endothelial derived mediators.