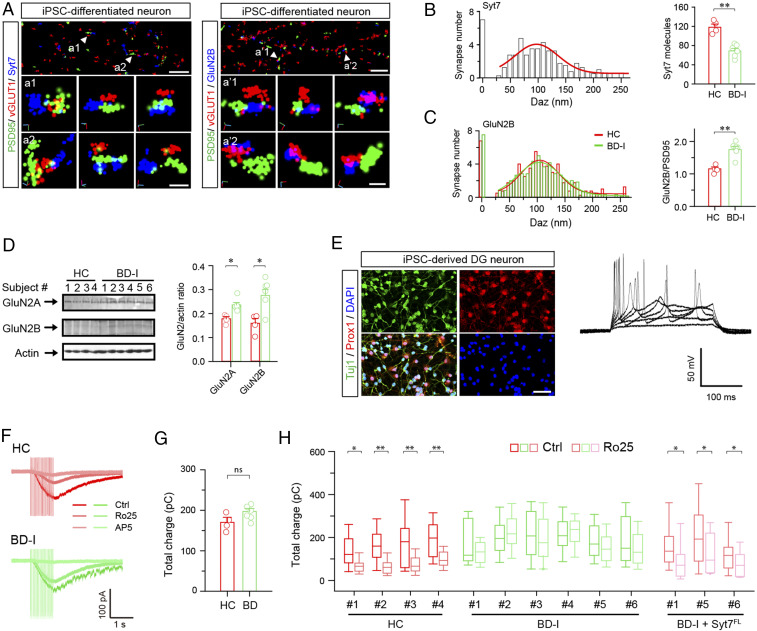
Fig. 6.
Syt7 and GluN2B deficits in patient iPSC-derived hippocampal DG-like neurons. (A) Sample STORM images showing localization of Syt7 (Left) and GluN2B (Right) in the synapses of healthy control (HC) iPSC-derived neurons. Arrowheads denote sample synapses. (B) Histograms showing localization of Syt7 in the synapses of HC neurons (Left) and Syt7 expression in HC and patient iPSC-derived neurons (Right). HC, n = 204 synapses/4 subjects; BD-I, n = 306/6. (C) Localization (Left) and quantitative analysis (Right) of GluN2B in the synapses detected by STORM. (D) Immunoblots (Left) and quantitative analysis (Right) of GluN2A/2B in the patient iPSC-derived DG-like neurons. HC, n = 4 lines; BD, n = 3 for LR and n = 3 for NR. (E) Characterization of patient iPSC-derived DG-like neurons. (Left) Sample immunostaining images showing Prox1+ expression in the iPSC-derived neurons. (Scale bar: 50 μm.) (Right) Sample traces showing evoked APs in Prox1+ neurons. (F) Sample traces of 1-s, 20-Hz train-triggered NMDAR-EPSCs recorded in patient iPSC-derived neurons in 0.2 mM Ca2+. (G) Comparison of NMDAR-EPSC charge transfer between the neurons of HC and patients. HC, n = 4 lines; BD-I, n = 6 lines. (H) Total charge transfer of NMDAR-EPSCs in HC neurons, BD-I neurons, and BD-I neurons overexpressing Syt7. HC, n = 13 to 51 for each cell line; BD-I, n = 17 to 43 for each cell line; BD-I + Syt7, n = 11 to 26 for each cell line. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.001, Student’s t test. Error bars represent SEM.