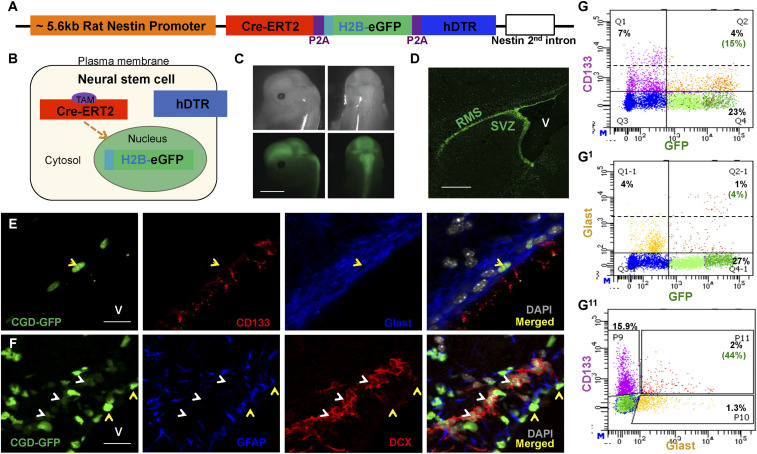
Fig. 1.
CGD transgene labels adult subventricular zone neural stem cells and progenitors. (A) Diagram of the transgene construct. Purple blocks represent the P2A ribosomal skipping element insulating the three gene cassettes. (B) Cartoon illustrates localization of the three transgene products in NSC: Cre-ERT2 in the cytosol, H2B-eGFP in the nucleus, and hDTR on the plasma membrane. (C) Transgene GFP imaging of a 14-d embryo undergoing neurogenesis illustrates CGD transgene expression in developing central nervous system (Scale bar, 3 mm.) (D) Enhanced transgene GFP expression in adult SVZ and rostral migratory stream (RMS). V: lateral ventricle. (Scale bar, 500 μm.) (E) Coronal section staining of 2-mo-old mouse SVZ shows colocalization of CGD-GFP with stem-cell markers CD133 and Glast. V: lateral ventricle. (Scale bar, 20 μm.) (F) Relationship between CGD-GFPhi and stem-cell marker GFAP versus GFPlo and progenitor marker DCX in a sagittal section of adult SVZ (Scale bar, 20 μm.) (G, G1, and G11) A small fraction of CGD-GFP+ cells in the SVZ express CD133 (G, 15%) or Glast (G1, 4%), and 44% of all CD133+Glast+ double-positive cells express CGD-GFP (G11). V: lateral ventricle. See also SI Appendix, Fig. S1.