Fig. 5.
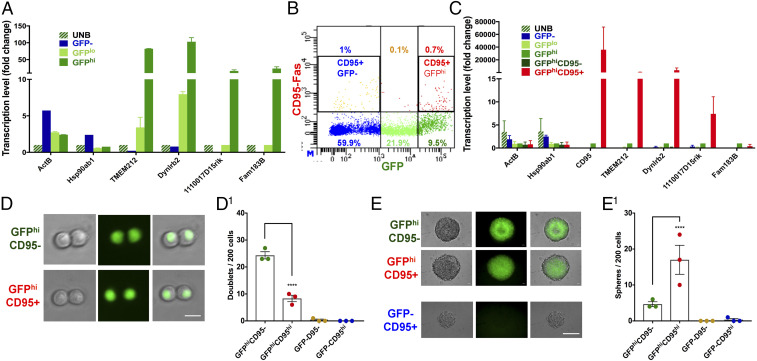
H0 cells have unique stem-like properties. (A) Expression of four H0-specific genes (Tmem212, Dynlrb2, Fam183b, and 1110017D15rik) was verified by qRT-PCR in single-cell sequencing samples. Gene expression levels were normalized to UNB cells. Mean ± SEM, n = 2. (B) CD95-Fas receptor antibody labels one subgroup of GFPhi and one subgroup of GFP– cells. All of the numbers represent the percentage of each population among the whole SVZ. (C) GFPhi;CD95+ cells have enriched expression of the H0-specific genes. qRT-PCR was performed with GFP and CD95 sorted cells for the H0-specific genes. Gene expression levels were normalized to GFPhi cells. Mean ± SEM, n = 2. (D and D1) Representative images and quantification of doublet formation by GFP and CD95 sorted cells at 24 h. Note that GFPhi;CD95– cells are more efficient at forming doublets (Scale bar, 10 μm.) (E and E1) Representative images and quantification of sphere formation of GFP and CD95 sorted cells. Note that, reminiscent of Fig. 2 C and D, GFPhi;CD95+ cells, which were inefficient in doublet formation at 24 h, are most efficient at forming neurospheres 6 d later. Note also that GFP–;CD95+ cells do not form neurospheres. (Scale bar, 100 μm.) Mean ± SEM, n = 3 biological replicate mice for each group in D and E1. **** in D1 and E1 indicates P values <0.0001. See also SI Appendix, Fig. S5.