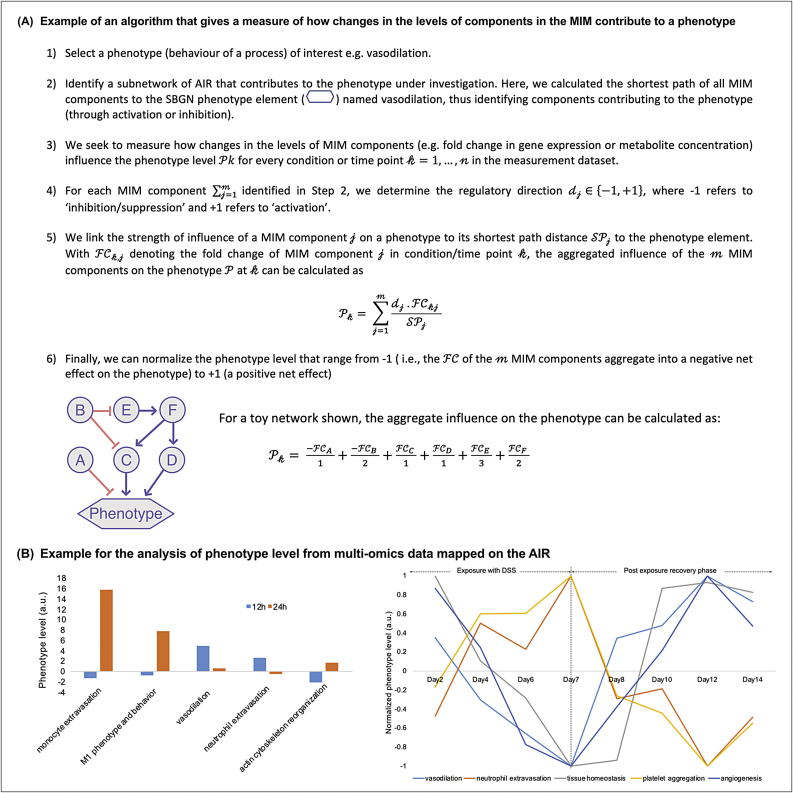
Fig. 6.
Examples using the AIR for bioinformatic analyses. (A) Algorithm to determine the aggregated influence of change in the MIM components on phenotype level. A toy network in the bottom highlights the aggregate influence on the phenotype due to the expression or concentration fold change in the network components A to F. (B) Examples for the analysis of phenotype level from multi-omics data mapped on the AIR. Left: An example where we measure the influence on the phenotype level (a.u.) from MIM components after mapping of miRNA log fold change data from the zymosan-induced peritonitis mouse model treated with/without resolvin D1 (RvD1) at time point 12 h and 24 h (Recchiuti et al., 2011). The bar in the plot indicates influence on the phenotype levels when RvD1 was co-administered. The graph indicates that vasodilation was quickly downregulated which is also supported by the low level of neutrophil extravasation. Other phenotypes (monocyte extravasation; M1 phenotype and behavior; acting cytoskeleton reorganization) were upregulated, suggesting that RvD1 brought the whole systems quickly towards the inflammation resolution phase in comparison to the exposure with zymosan alone. Right: In another example, we highlight the influence of MIM components on various processes associated with the acute inflammation onset and resolution after mapping of time-series transcriptomics profile from mouse colitis model (Czarnewski et al., 2019). The graph indicates normalized phenotype levels (‘vasodilation’, ‘neutrophil extravasation’, ‘tissue homeostasis’, ‘platelet aggregation’, and ‘angiogenesis’) from mouse model exposed with dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) for 7 days to induce acute colitis followed by 7 days of recovery phase. In this study transcriptomics profiling of colon samples were carried out for 9 different timepoints (Day 0, Day 2, Day 4, Day 6, Day 7, Day 8, Day 10, Day 12 and Day 14). Results suggest that the ‘neutrophil extravasation’ and ‘platelet aggregation’ increases until the DSS exposure (i.e. 7days, inflammation initiation phase) followed by sharp decline during the post exposure recovery phase. On the other hand, ‘vasodilation’ increases from day 7–12 (inflammation transition phase) and then a sharp decline in the phenotype was observed suggesting that the system is in inflammation resolution phase.