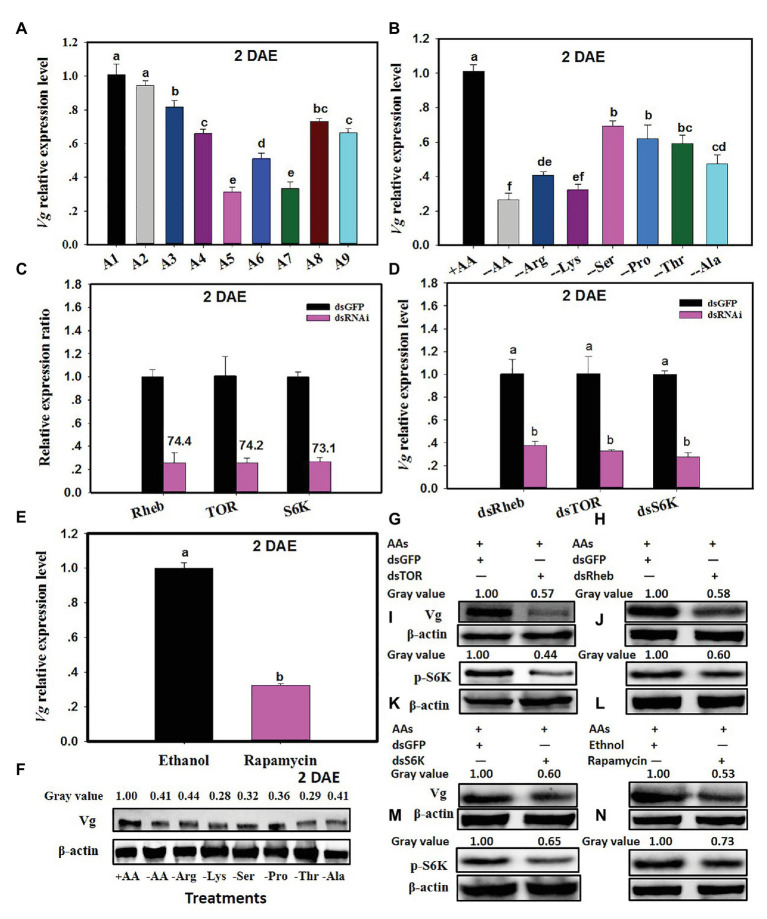
Figure 3.
The TOR pathway transduces AA signals and regulates vitellogenin (Vg) synthesis. Panel (A) shows Vg expression in C. lividipennis females supplied with diets A1–A9 (as defined in Figure 1 legend); (B) shows Vg expression on artificial diets that vary in AAs (as defined in Figure 2 legend). Panel (C) illustrates the relative expression ratios of Rheb, TOR, and S6K in C. lividipennis females treated with dsRheb, dsTOR, and dsS6K, respectively. dsGFP was transfected as a negative control. Panel (D) shows mean Vg expression in C. lividipennis females treated with dietary dsRheb, dsTOR, and dsS6K. Panel (E) shows Vg expression in C. lividipennis females treated with rapamycin and ethanol (control). Panel (F) shows the Vg protein levels in adult females (n = 15) as determined by western blots with anti-Vg antiserum. Each treatment and control represent three independent biological replicates, and error bars show means ± SEM. Different lowercase letters in the histogram indicate significant differences at p < 0.05 (Student’s t-test). Panels (G–N) show Vg protein levels and pS6K phosphorylation status in C. lividipennis treated with dsRheb, dsTOR, dsS6K, and rapamycin. Proteins were detected with anti-Vg or anti-pS6K antisera and visualized by western blot analysis. Antiserum to β-actin was used as a loading control.